-
 Biosynthesis of the Inner Core of Bordetella pertussis Lipopolysaccharides: Effect of Mutations on LPS Structure, Cell Division, and Toll-like Receptor 4 Activation
Biosynthesis of the Inner Core of Bordetella pertussis Lipopolysaccharides: Effect of Mutations on LPS Structure, Cell Division, and Toll-like Receptor 4 Activation -
 APOBEC3G Is a p53-Dependent Restriction Factor in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection of Human Cells Included in the p53/Immune Axis
APOBEC3G Is a p53-Dependent Restriction Factor in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection of Human Cells Included in the p53/Immune Axis -
 Molecular Profiling of Lymphatic Endothelial Cell Activation In Vitro
Molecular Profiling of Lymphatic Endothelial Cell Activation In Vitro -
 ZNF643/ZFP69B Exerts Oncogenic Properties and Associates with Cell Adhesion and Immune Processes
ZNF643/ZFP69B Exerts Oncogenic Properties and Associates with Cell Adhesion and Immune Processes -
 Sperm Chromatin Status and DNA Fragmentation in Mouse Species with Divergent Mating Systems
Sperm Chromatin Status and DNA Fragmentation in Mouse Species with Divergent Mating Systems
Journal Description
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal providing an advanced forum for biochemistry, molecular and cell biology, molecular biophysics, molecular medicine, and all aspects of molecular research in chemistry, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Australian Society of Plant Scientists (ASPS), Epigenetics Society, European Calcium Society (ECS), European Chitin Society (EUCHIS), Spanish Society for Cell Biology (SEBC) and others are affiliated with IJMS and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, MEDLINE, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Inorganic Chemistry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about the IJMS.
- Companion journals for IJMS include: Biophysica, Obesities, Stresses and Lymphatics.
Impact Factor:
5.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
6.2 (2022)
Latest Articles
The Potentiality of Natural Products and Herbal Medicine as Novel Medications for Parkinson’s Disease: A Promising Therapeutic Approach
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1071; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021071 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
As the global population ages, the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is steadily on the rise. PD demonstrates chronic and progressive characteristics, and many cases can transition into dementia. This increases societal and economic burdens, emphasizing the need to find effective treatments. Among
[...] Read more.
As the global population ages, the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is steadily on the rise. PD demonstrates chronic and progressive characteristics, and many cases can transition into dementia. This increases societal and economic burdens, emphasizing the need to find effective treatments. Among the widely recognized causes of PD is the abnormal accumulation of proteins, and autophagy dysfunction accelerates this accumulation. The resultant Lewy bodies are also commonly found in Alzheimer’s disease patients, suggesting an increased potential for the onset of dementia. Additionally, the production of free radicals due to mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to neuronal damage and degeneration. The activation of astrocytes and the M1 phenotype of microglia promote damage to dopamine neurons. The drugs currently used for PD only delay the clinical progression and exacerbation of the disease without targeting its root cause, and come with various side effects. Thus, there is a demand for treatments with fewer side effects, with much potential offered by natural products. In this study, we reviewed a total of 14 articles related to herbal medicines and natural products and investigated their relevance to possible PD treatment. The results showed that the reviewed herbal medicines and natural products are effective against lysosomal disorder, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation, key mechanisms underlying PD. Therefore, natural products and herbal medicines can reduce neurotoxicity and might improve both motor and non-motor symptoms associated with PD. Furthermore, these products, with their multi-target effects, enhance bioavailability, inhibit antibiotic resistance, and might additionally eliminate side effects, making them good alternative therapies for PD treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Concepts, New Perspectives, and Current Therapies for Parkinson's Disease)
Open AccessArticle
Ontogeny of the Cytochrome P450 Superfamily in the Ornate Spiny Lobster (Panulirus ornatus)
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1070; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021070 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Cytochrome P450s (CYP450s) are a versatile superfamily of enzymes known to undergo rapid evolution. They have important roles across growth and development pathways in crustaceans, although it is difficult to characterise orthologs between species due to their sequence diversity. Conserved CYP450s enzymes in
[...] Read more.
Cytochrome P450s (CYP450s) are a versatile superfamily of enzymes known to undergo rapid evolution. They have important roles across growth and development pathways in crustaceans, although it is difficult to characterise orthologs between species due to their sequence diversity. Conserved CYP450s enzymes in crustaceans are those associated with ecdysteroidogenesis: synthesising and breaking down the active moult hormone, 20-hydroxyecdysone. The complex life cycle of the ornate spiny lobster, Panulirus ornatus, relies on moulting in order to grow and develop. Many of these diverse life stages have been analysed to establish a comprehensive transcriptomic database for this species. The transcripts putatively encoding for CYP450s were mapped using transcriptomic analysis and identified across growth and development stages. With the aid of phylogeny, 28 transcripts of 42 putative P. ornatus CYP450s were annotated, including the well conserved Halloween genes, which are involved in ecdysteroidogenesis. Expression patterns across the life stages determined that only a subset of the CYP450s can be detected in each life stage or tissue. Four Shed transcripts show overlapping expression between metamorphosis and adult tissues, suggesting pleotropic functions of the multiple Shed orthologs within P. ornatus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Neuropeptides and Endocrine Regulations in Insects and Crustaceans)
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicity, Cellular Imaging, Molecular Docking, and ADMET Studies of Piperazine-Linked 1,8-Naphthalimide-Arylsulfonyl Derivatives
by
, , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1069; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021069 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
To reduce the mortality and morbidity associated with cancer, new cancer theranostics are in high demand and are an emerging area of research. To achieve this goal, we report the synthesis and characterization of piperazine-linked 1,8-naphthalimide-arylsulfonyl derivatives (SA1–SA7). These compounds were synthesized in
[...] Read more.
To reduce the mortality and morbidity associated with cancer, new cancer theranostics are in high demand and are an emerging area of research. To achieve this goal, we report the synthesis and characterization of piperazine-linked 1,8-naphthalimide-arylsulfonyl derivatives (SA1–SA7). These compounds were synthesized in good yields following a two-step protocol and characterized using multiple analytical techniques. In vitro cytotoxicity and fluorescent cellular imaging of the compounds were assessed against non-cancerous fibroblast (3T3) and breast cancer (4T1) cell lines. Although the former study indicated the safe nature of the compounds (viability = 82–95% at 1 μg/mL), imaging studies revealed that the designed probes had good membrane permeability and could disperse in the whole cell cytoplasm. In silico studies, including molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, and ADME/Tox results, indicated that the compounds had the ability to target CAIX-expressing cancers. These findings suggest that piperazine-linked 1,8-naphthalimide-arylsulfonyl derivatives are potential candidates for cancer theranostics and a valuable backbone for future research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Functional Molecules in Tracing and Cancer Therapeutics)
Open AccessReview
The Multifaceted Role of FUT8 in Tumorigenesis: From Pathways to Potential Clinical Applications
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1068; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021068 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
FUT8, the sole glycosyltransferase responsible for N-glycan core fucosylation, plays a crucial role in tumorigenesis and development. Aberrant FUT8 expression disrupts the function of critical cellular components and triggers the abnormality of tumor signaling pathways, leading to malignant transformations such as proliferation, invasion,
[...] Read more.
FUT8, the sole glycosyltransferase responsible for N-glycan core fucosylation, plays a crucial role in tumorigenesis and development. Aberrant FUT8 expression disrupts the function of critical cellular components and triggers the abnormality of tumor signaling pathways, leading to malignant transformations such as proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and immunosuppression. The association between FUT8 and unfavorable outcomes in various tumors underscores its potential as a valuable diagnostic marker. Given the remarkable variation in biological functions and regulatory mechanisms of FUT8 across different tumor types, gaining a comprehensive understanding of its complexity is imperative. Here, we review how FUT8 plays roles in tumorigenesis and development, and how this outcome could be utilized to develop potential clinical therapies for tumors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advance in Cancer Biomarker: From Molecular Mechanisms to Potential Therapy)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The TGF-β Family in Glioblastoma
by
and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1067; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021067 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Members of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family have been implicated in the biology of several cancers. In this review, we focus on the role of TGFβ and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling in glioblastoma. Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common malignant
[...] Read more.
Members of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family have been implicated in the biology of several cancers. In this review, we focus on the role of TGFβ and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling in glioblastoma. Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common malignant brain tumor in adults; it presents at a median age of 64 years, but can occur at any age, including childhood. Unfortunately, there is no cure, and even patients undergoing current treatments (surgical resection, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy) have a median survival of 15 months. There is a great need to identify new therapeutic targets to improve the treatment of GBM patients. TGF-βs signaling promotes tumorigenesis in glioblastoma, while BMPs suppress tumorigenic potential by inducing tumor cell differentiation. In this review, we discuss the actions of TGF-βs and BMPs on cancer cells as well as in the tumor microenvironment, and their use in potential therapeutic intervention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Oncology)
Open AccessReview
Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles and Organoids: A Prospective Advanced Model for Pancreatic Cancer Research
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1066; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021066 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer, notorious for its grim 10% five-year survival rate, poses significant clinical challenges, largely due to late-stage diagnosis and limited therapeutic options. This review delves into the generation of organoids, including those derived from resected tissues, biopsies, pluripotent stem cells, and adult
[...] Read more.
Pancreatic cancer, notorious for its grim 10% five-year survival rate, poses significant clinical challenges, largely due to late-stage diagnosis and limited therapeutic options. This review delves into the generation of organoids, including those derived from resected tissues, biopsies, pluripotent stem cells, and adult stem cells, as well as the advancements in 3D printing. It explores the complexities of the tumor microenvironment, emphasizing culture media, the integration of non-neoplastic cells, and angiogenesis. Additionally, the review examines the multifaceted properties of graphene oxide (GO), such as its mechanical, thermal, electrical, chemical, and optical attributes, and their implications in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. GO’s unique properties facilitate its interaction with tumors, allowing targeted drug delivery and enhanced imaging for early detection and treatment. The integration of GO with 3D cultured organoid systems, particularly in pancreatic cancer research, is critically analyzed, highlighting current limitations and future potential. This innovative approach has the promise to transform personalized medicine, improve drug screening efficiency, and aid biomarker discovery in this aggressive disease. Through this review, we offer a balanced perspective on the advancements and future prospects in pancreatic cancer research, harnessing the potential of organoids and GO.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Therapeutic Targets in Pancreatic Cancer)
Open AccessBrief Report
Whole-Exome Screening and Analysis of Signaling Pathways in Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 Patients with Different Outcomes: Insights into Cellular Mechanisms and Possible Functional Implications
by
, , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1065; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021065 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a syndrome characterized by tumors in multiple organs. Although being a dominantly inherited monogenic disease, disease phenotypes are unpredictable and differ even among members of the same family. There is growing evidence for the role of
[...] Read more.
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is a syndrome characterized by tumors in multiple organs. Although being a dominantly inherited monogenic disease, disease phenotypes are unpredictable and differ even among members of the same family. There is growing evidence for the role of modifier genes in the alteration of the course of this disease. However, genome-wide screening data are still lacking. In our study, we addressed the different outcomes of the disease, focusing on pituitary and adrenocortical tumors. By means of exome sequencing we identified the affected signaling pathways that segregated with those symptoms. Most significantly, we identified damaging alterations in numerous structural genes responsible for cell adhesion and migration. Additionally, in the case of pituitary tumors, genes related to neuronal function, survival, and morphogenesis were repeatedly identified, while in patients with adrenocortical tumors, TLR10, which is involved in the regulation of the innate immunity, was commonly modified. Our data show that using exome screening, it is possible to find signatures which correlate with the given clinical MEN1 outcomes, providing evidence that studies addressing modifier effects in MEN1 are reasonable.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Endocrinology and Metabolism)
Open AccessReview
Molecular Targeting of the Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2 (HER2) Genes across Various Cancers
by
, , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1064; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021064 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) belongs to the ErbB family, a group of four transmembrane glycoproteins with tyrosine kinase activity, all structurally related to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). These tyrosine kinases are involved in the transmission of cellular signals controlling
[...] Read more.
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) belongs to the ErbB family, a group of four transmembrane glycoproteins with tyrosine kinase activity, all structurally related to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). These tyrosine kinases are involved in the transmission of cellular signals controlling normal cell growth and differentiation. If this transmission goes awry, it can lead to dysregulated growth of the cell. HER2 specifically can be implicated in the pathogenesis of at least eight malignancies. HER2 positivity quickly became a well-characterized indicator of aggressiveness and poor prognosis, with high rates of disease progression and mortality. After realizing the implication of HER2, it first became investigated as a target for treatment in breast cancer, and later expanded to areas of research in other cancer types. To this day, the most therapeutic advancements of anti-HER2 therapy have been in breast cancer; however, there have been strong advancements made in the incorporation of anti-HER2 therapy in other cancer types as well. This comprehensive review dissects HER2 to its core, incorporating the most up to date information. The topics touched upon are discussed in detail and up to 200 published sources from the most highly recognized journals have been integrated. The importance of knowing about HER2 is exemplified by the groundbreaking advancements that have been made, and the change in treatment plans it has brought to the oncological world in the last twenty years. Since its groundbreaking discovery there have been significant breakthroughs in knowledge regarding the actual receptor, the receptors biology, its mechanism of action, and advancements in tests to detect HER2 and significant strides on how to best incorporate targeted treatment. Due to the success of this field thus far, the review concludes by discussing the future of novel anti-HER2 therapy currently in development that everyone should be aware of.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue From Basic Science to Treatment Strategies: Personalized Cancer Therapy)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Resistance to Combined Anthracycline–Taxane Chemotherapy Is Associated with Altered Metabolism and Inflammation in Breast Carcinomas
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1063; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021063 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Approximately 30% of early-stage breast cancer (BC) patients experience recurrence after systemic chemotherapy; thus, understanding therapy resistance is crucial in developing more successful treatments. Here, we investigated the mechanisms underlying resistance to combined anthracycline–taxane treatment by comparing gene expression patterns with subsequent therapeutic
[...] Read more.
Approximately 30% of early-stage breast cancer (BC) patients experience recurrence after systemic chemotherapy; thus, understanding therapy resistance is crucial in developing more successful treatments. Here, we investigated the mechanisms underlying resistance to combined anthracycline–taxane treatment by comparing gene expression patterns with subsequent therapeutic responses. We established a cohort of 634 anthracycline–taxane-treated patients with pathological complete response (PCR) and a separate cohort of 187 patients with relapse-free survival (RFS) data, each having transcriptome-level expression data of 10,017 unique genes. Patients were categorized as responders and non-responders based on their PCR and RFS status, and the expression for each gene was compared between the two groups using a Mann–Whitney U-test. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05, with fold change (FC) > 1.44. Altogether, 224 overexpressed genes were identified in the tumor samples derived from the patients without PCR; among these, the gene sets associated with xenobiotic metabolism (e.g., CYP3A4, CYP2A6) exhibited significant enrichment. The genes ORAI3 and BCAM differentiated non-responders from responders with the highest AUC values (AUC > 0.75, p < 0.0001). We identified 51 upregulated genes in the tumor samples derived from the patients with relapse within 60 months, participating primarily in inflammation and innate immune responses (e.g., LYN, LY96, ANXA1). Furthermore, the amino acid transporter SLC7A5, distinguishing non-responders from responders, had significantly higher expression in tumors and metastases than in normal tissues (Kruskal–Wallis p = 8.2 × 10−20). The identified biomarkers underscore the significance of tumor metabolism and microenvironment in treatment resistance and can serve as a foundation for preclinical validation studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances and Mechanisms in Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Differences in Troponin I and Troponin T Release in High-Performance Athletes Outside of Competition
by
, , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1062; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021062 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Troponin I and troponin T are critical biomarkers for myocardial infarction and damage and are pivotal in cardiological and laboratory diagnostics, including emergency settings. Rapid testing protocols have been developed for urgent care, particularly in emergency outpatient clinics. Studies indicate that strenuous physical
[...] Read more.
Troponin I and troponin T are critical biomarkers for myocardial infarction and damage and are pivotal in cardiological and laboratory diagnostics, including emergency settings. Rapid testing protocols have been developed for urgent care, particularly in emergency outpatient clinics. Studies indicate that strenuous physical activity can cause transient increases in these troponin levels, which are typically considered benign. This research focused on 219 elite athletes from national teams, evaluating their troponin I and T levels as part of routine sports medical exams, independent of competition-related physical stress. The results showed that 9.2% (18 athletes) had elevated troponin I levels above the reporting threshold, while their troponin T levels remained within the normal range. Conversely, only 0.9% (two athletes) had normal troponin I but raised troponin T levels, and 2.3% (five athletes) exhibited increases in both markers. No significant cardiovascular differences were noted between those with elevated troponin levels and those without. This study concludes that elevated troponin I is a common response to the intense physical training endured by high-performance endurance athletes, whereas troponin T elevation does not seem to be directly linked to physical exertion in this group. For cardiac assessments, particularly when ruling out cardiac damage in these athletes, troponin T might be a more reliable indicator than troponin I.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Research on Cardiac Troponin)
Open AccessEditorial
Special Issue “Neurogenetics in Neurology”
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1061; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021061 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
With the rapid developments in molecular genetics and genomics, this Special Issue collates works outlining ultra-modern scientific research [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Neurogenetics in Neurology)
Open AccessArticle
Glutaredoxin 2 Protein (Grx2) as an Independent Prognostic Factor Associated with the Survival of Colon Adenocarcinoma Patients
by
, , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1060; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021060 (registering DOI) - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Glutaredoxin 2 (Grx2; Glrx2) is a glutathione-dependent oxidoreductase located in mitochondria, which is central to the regulation of glutathione homeostasis and mitochondrial redox, and plays a crucial role in highly metabolic tissues. In response to mitochondrial redox signals and oxidative stress, Grx2 can
[...] Read more.
Glutaredoxin 2 (Grx2; Glrx2) is a glutathione-dependent oxidoreductase located in mitochondria, which is central to the regulation of glutathione homeostasis and mitochondrial redox, and plays a crucial role in highly metabolic tissues. In response to mitochondrial redox signals and oxidative stress, Grx2 can catalyze the oxidation and S-glutathionylation of membrane-bound thiol proteins in mitochondria. Therefore, it can have a significant impact on cancer development. To investigate this further, we performed an immunohistochemical analysis of Grx2 protein expression in colon adenocarcinoma samples collected from patients with primary colon adenocarcinoma (stage I and II) and patients with metastasis to regional lymph nodes (stage III). The results of our study revealed a significant relationship between the immunohistochemical expression of Grx2 and tumor histological grade, depth of invasion, regional lymph node involvement, angioinvasion, staging, and PCNA immunohistochemical expression. It was found that 87% of patients with stage I had high levels of Grx2 expression. In contrast, only 33% of patients with stage II and 1% of patients with stage III had high levels of Grx2 expression. Moreover, the multivariate analysis revealed that the immunohistochemical expression of Grx2 protein apart from the grade of tumor differentiation was an independent prognostic factors for the survival of patients with colon adenocarcinoma. Studies analyzing Grx2 levels in patients’ blood confirmed that the highest levels of serum Grx2 protein was also found in stage I patients, which was reflected in the survival curves. A higher level of Grx2 in the serum has been associated with a more favorable outcome. These results were supported by in vitro analysis conducted on colorectal cancer cell lines that corresponded to stages I, II, and III of colorectal cancer, using qRT-PCR and Western Blot.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Research on Biomarkers in Gastrointestinal Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Metabolomics Approach Reveals the Dynamic Variations of Metabolites and Bioactivities in Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ Leaves during Development
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1059; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021059 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ is widely cultivated in China for its ornamental, medicinal, and edible properties. The whole plant of tree peony is rich in bioactive substances, while the comprehensive understanding of metabolites in the leaves is limited. In this study, an untargeted
[...] Read more.
Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ is widely cultivated in China for its ornamental, medicinal, and edible properties. The whole plant of tree peony is rich in bioactive substances, while the comprehensive understanding of metabolites in the leaves is limited. In this study, an untargeted metabolomics strategy based on UPLC-ESI-TOF-MS was conducted to analyze the dynamic variations of bioactive metabolites in P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ leaves during development. A total of 321 metabolites were rapidly annotated based on the GNPS platform, in-house database, and publications. To accurately quantify the selected metabolites, a targeted method of HPLC-ESI-QQQ-MS was used. Albiflorin, paeoniflorin, pentagalloylglucose, luteolin 7-glucoside, and benzoylpaeoniflorin were recognized as the dominant bioactive compounds with significant content variations during leaf development. Metabolite variations during the development of P. ostii ‘Feng Dan’ leaves are greatly attributed to the variations in antioxidant activities. Among all tested bacteria, the leaf extract exhibited exceptional inhibitory effects against Streptococcus hemolytis-β. This research firstly provides new insights into tree peony leaves during development. The stages of S1–S2 may be the most promising harvesting time for potential use in food or pharmaceutical purposes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bioactives and Nutraceuticals)
►▼
Show Figures
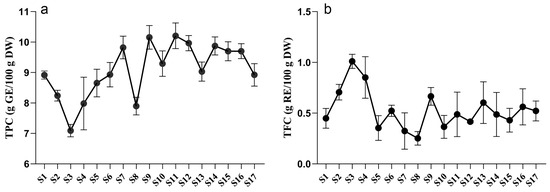
Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Samak et al. Dysregulation of Krüppel-like Factor 2 and Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2D Drive Cardiac Microvascular Inflammation and Dysfunction in Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2482
by
, , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1058; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021058 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
In the original publication [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Pathways in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Acetyltransferase P300 Regulates Glucose Metabolic Reprogramming through Catalyzing Succinylation in Lung Cancer
by
, , , , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1057; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021057 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Aberrant protein post-translational modification is a hallmark of malignant tumors. Lysine succinylation (Ksucc) plays a vital role in cell energy metabolism in various cancers. However, whether succinylation can be catalyzed by acetyltransferase p300 remains unclear. In this study, we unveiled that p300 is
[...] Read more.
Aberrant protein post-translational modification is a hallmark of malignant tumors. Lysine succinylation (Ksucc) plays a vital role in cell energy metabolism in various cancers. However, whether succinylation can be catalyzed by acetyltransferase p300 remains unclear. In this study, we unveiled that p300 is a “writer” for succinylation, and p300-mediated Ksucc promotes cell glycometabolism in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Specifically, our succinylome data revealed that EP300 deficiency leads to the systemic reduction of Ksucc, and 79.55% of the p300-succinylated proteins were found in the cytoplasm, which were primarily enriched in the carbohydrate metabolism process. Interestingly, deleting EP300 led to a notable decrease in Ksucc levels on several glycolytic enzymes, especially Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1 (PGK1). Mutation of the succinylated site of PGK1 notably hindered cell glycolysis and lactic acid excretion. Metabolomics in vivo indicated that p300-caused metabolic reprogramming was mainly attributed to the altered carbohydrate metabolism. In addition, 89.35% of LUAD patients exhibited cytoplasmic localization of p300, with higher levels in tumor tissues than adjacent normal tissues. High levels of p300 correlated with advanced tumor stages and poor prognosis of LUAD patients. Briefly, we disclose the activity of p300 to catalyze succinylation, which contributes to cell glucose metabolic reprogramming and malignant progression of lung cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Immunology)
►▼
Show Figures
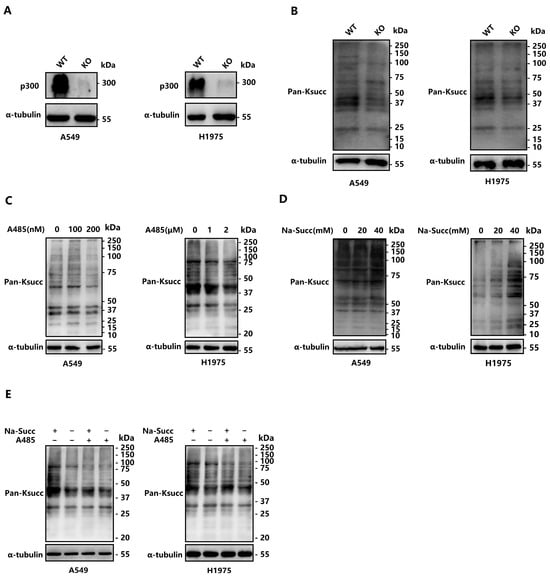
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Mismatch Repair Deficiency as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Endometrial Cancer: A Review on Immunohistochemistry Staining Patterns and Clinical Implications
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1056; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021056 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Among the four endometrial cancer (EC) TCGA molecular groups, the MSI/hypermutated group represents an important percentage of tumors (30%), including different histotypes, and generally confers an intermediate prognosis for affected women, also providing new immunotherapeutic strategies. Immunohistochemistry for MMR proteins (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6
[...] Read more.
Among the four endometrial cancer (EC) TCGA molecular groups, the MSI/hypermutated group represents an important percentage of tumors (30%), including different histotypes, and generally confers an intermediate prognosis for affected women, also providing new immunotherapeutic strategies. Immunohistochemistry for MMR proteins (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2) has become the optimal diagnostic MSI surrogate worldwide. This review aims to provide state-of-the-art knowledge on MMR deficiency/MSI in EC and to clarify the pathological assessment, interpretation pitfalls and reporting of MMR status.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Gynecological Cancer: Targeted Therapeutics and Future Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures
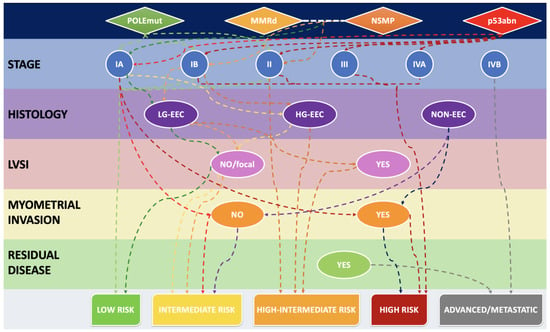
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Impact of Cesarean Section Delivery on Intestinal Microbiota: Mechanisms, Consequences, and Perspectives—A Systematic Review
by
, , , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1055; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021055 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The relationship between cesarean section (CS) delivery and intestinal microbiota is increasingly studied. CS-born infants display distinct gut microbial compositions due to the absence of maternal birth canal microorganisms. These alterations potentially link to long-term health implications like immune-related disorders and allergies. This
[...] Read more.
The relationship between cesarean section (CS) delivery and intestinal microbiota is increasingly studied. CS-born infants display distinct gut microbial compositions due to the absence of maternal birth canal microorganisms. These alterations potentially link to long-term health implications like immune-related disorders and allergies. This correlation underscores the intricate connection between birth mode and the establishment of diverse intestinal microbiota. A systematic literature review was conducted on the PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases by analyzing the articles and examining the intricate interactions between CS delivery and the infant’s intestinal microbiota. The analysis, based on a wide-ranging selection of studies, elucidates the multifaceted dynamics involved in CS-associated shifts in the establishment of fetal microbiota. We also explore the potential ramifications of these microbial changes on neonatal health and development, providing a comprehensive overview for clinicians and researchers. By synthesizing current findings, this review contributes to a deeper understanding of the interplay between delivery mode and early microbial colonization, paving the way for informed clinical decisions and future investigations in the field of perinatal medicine.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Gut Microbiota in Human Health)
►▼
Show Figures
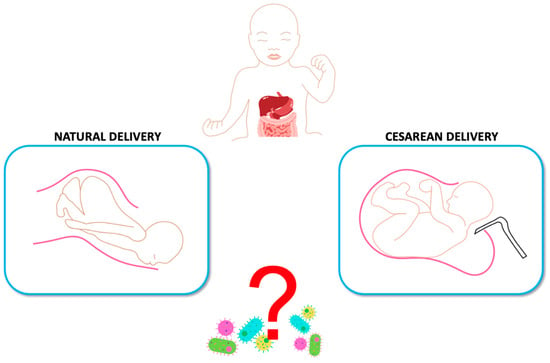
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal Changes in Cell Homeostasis and Energy Metabolism in Trachinotus ovatus in Response to Acute Hypoxic Stress
by
, , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1054; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021054 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Trachinotus ovatus is an economically important mariculture fish, and hypoxia has become a critical threat to this hypoxia-sensitive species. However, the molecular adaptation mechanism of T. ovatus liver to hypoxia remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the effects of acute hypoxic stress
[...] Read more.
Trachinotus ovatus is an economically important mariculture fish, and hypoxia has become a critical threat to this hypoxia-sensitive species. However, the molecular adaptation mechanism of T. ovatus liver to hypoxia remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the effects of acute hypoxic stress (1.5 ± 0.1 mg·L−1 for 6 h) and re-oxygenation (5.8 ± 0.3 mg·L−1 for 12 h) in T. ovatus liver at both the transcriptomic and metabolic levels to elucidate hypoxia adaptation mechanism. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analyses identified 36 genes and seven metabolites as key molecules that were highly related to signal transduction, cell growth and death, carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and lipid metabolism, and all played key roles in hypoxia adaptation. Of these, the hub genes FOS and JUN were pivotal hypoxia adaptation biomarkers for regulating cell growth and death. During hypoxia, up-regulation of GADD45B and CDKN1A genes induced cell cycle arrest. Enhancing intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in combination with glutathione metabolism triggered apoptosis; meanwhile, anti-apoptosis mechanism was activated after hypoxia. Expression of genes related to glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, amino acid metabolism, fat mobilization, and fatty acid biosynthesis were up-regulated after acute hypoxic stress, promoting energy supply. After re-oxygenation for 12 h, continuous apoptosis favored cellular function and tissue repair. Shifting from anaerobic metabolism (glycolysis) during hypoxia to aerobic metabolism (fatty acid β-oxidation and TCA cycle) after re-oxygenation was an important energy metabolism adaptation mechanism. Hypoxia 6 h was a critical period for metabolism alteration and cellular homeostasis, and re-oxygenation intervention should be implemented in a timely way. This study thoroughly examined the molecular response mechanism of T. ovatus under acute hypoxic stress, which contributes to the molecular breeding of hypoxia-tolerant cultivars.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism of the Intermediate Secondary Growth and Internode Elongation of the Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.) by the Combined Analysis of the Transcriptome and Metabolome
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1053; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021053 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The length of internodes plays a crucial role in determining the height of the castor plant (Ricinus communis L.). However, the specific mechanisms underlying internode elongation, particularly in the main stem of the castor plant, remain uncertain. To further investigate this, we
[...] Read more.
The length of internodes plays a crucial role in determining the height of the castor plant (Ricinus communis L.). However, the specific mechanisms underlying internode elongation, particularly in the main stem of the castor plant, remain uncertain. To further investigate this, we conducted a study focusing on the internode tissue of the dwarf castor variety 071113, comparing it with the control high-stalk Zhuansihao. Our study included a cytological observation, physiological measurement, transcriptome sequencing, and metabolic determination. Our integrated findings reveal that the dwarf variety 071113 undergoes an earlier lignification development in the main stem and has a more active lignin synthesis pathway during internode intermediate development. In addition, the dwarf variety exhibited lower levels of the plant hormone indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), which had an impact on the development process. Furthermore, we identified specific enzymes and regulators that were enriched in the pathways of the cell cycle, auxin signal transduction, and secondary cell wall synthesis. Using these findings, we developed a model that explained the intermediate secondary growth observed in castor internode elongation and enhanced our comprehension of the dwarfing mechanism of the 071113 variety. This research provides a theoretical groundwork for the future breeding of dwarf castor varieties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Plant Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Cytokine and Chemokine Level in Tear Film in Keratoconus Patients before and after Corneal Cross-Linking (CXL) Treatment
by
, , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25(2), 1052; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25021052 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Keratoconus (KC) is a degenerative corneal disorder whose aetiology remains unknown. The aim of our study was to analyse the expressions of cytokines and chemokines in KC patients before and after specified time intervals after corneal cross-linking (CXL) treatment to better understand the
[...] Read more.
Keratoconus (KC) is a degenerative corneal disorder whose aetiology remains unknown. The aim of our study was to analyse the expressions of cytokines and chemokines in KC patients before and after specified time intervals after corneal cross-linking (CXL) treatment to better understand the molecular mechanisms occurring before and after CXL in KC patients process of corneal regeneration.; Tear samples were gathered from 52 participants immediately after the CXL procedure and during the 12-month follow-up period. All patients underwent a detailed ophthalmological examination and tear samples were collected before and after CXL at regular intervals: 1 day before and after the surgery, at the day 7 visit, and at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after CXL. The control group consisted of 20 healthy people. 10 patients were women (50%) and 10 were men (50%). The mean age was 30 ± 3 years of age. Tear analysis was performed using the Bio-Plex 3D Suspension Array System. Corneal topography parameters measured by Scheimpflug Camera included: keratometry values (Ks, Kf), PI-Apex, PI-Thinnest, Cylinder.; All the 12 months post-op values of the KC patients’ topographic measurements were significantly lower than the pre-op. As for the tear cytokine levels comparison between the patient and control groups, cytokine levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and CXCL-10, among others, were detected in lower amounts in the KC group. The pre-op level of IL-6 exhibited a significant increase the day after CXL, whereas comparing the day after the procedure to 12 months after CXL, this showed a significant decrease. Both TNF-α and IL-1 showed a significant decrease compared to the day before and after CXL. We observed significantly higher levels of IL-1β, IL-10, IFN-γ and TNF-α in moderate and severe keratoconus than in mild keratoconus (p < 0.05). We also demonstrated a statistically significant positive correlation between both pre-op and 12 months after CXL TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6 and Ks and Kf values (p < 0.05, r > 0); Alterations of inflammatory mediators in tear fluid after CXL link with topographic changes and may contribute to the development and progression of KC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Pathology, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- IJMS Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Vol. 25 (2024)
- Vol. 24 (2023)
- Vol. 23 (2022)
- Vol. 22 (2021)
- Vol. 21 (2020)
- Vol. 20 (2019)
- Vol. 19 (2018)
- Vol. 18 (2017)
- Vol. 17 (2016)
- Vol. 16 (2015)
- Vol. 15 (2014)
- Vol. 14 (2013)
- Vol. 13 (2012)
- Vol. 12 (2011)
- Vol. 11 (2010)
- Vol. 10 (2009)
- Vol. 9 (2008)
- Vol. 8 (2007)
- Vol. 7 (2006)
- Vol. 6 (2005)
- Vol. 5 (2004)
- Vol. 4 (2003)
- Vol. 3 (2002)
- Vol. 2 (2001)
- Vol. 1 (2000)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Chemistry, IJMS, Mathematics, Symmetry, Computation
Molecular Topology and Computation
Topic Editors: Lorentz Jäntschi, Dusanka JanezicDeadline: 1 February 2024
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Cells, Diagnostics, IJMS, JCM, Pathogens, Pathophysiology
Applied Sciences and Technologies for Detection and Therapies of Pathologies in the Neuronal Environment
Topic Editors: Muh-Shi Lin, Hong Jiang, Yu-Yo SunDeadline: 29 February 2024
Topic in
Biomolecules, Cells, Genes, IJMS, ncRNA
MicroRNA: Mechanisms of Action, Physio-Pathological Implications, and Disease Biomarkers, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Y-h. Taguchi, Hsiuying WangDeadline: 20 April 2024
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cells, IJMS, Life, Oxygen
Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Mohamad Allaw, Ines Castangia, Maria Letizia Manca, Matteo Perra, Amparo NacherDeadline: 31 May 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
IJMS
Recent Developments and Updates in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Guest Editor: Spiros VlahopoulosDeadline: 20 January 2024
Special Issue in
IJMS
Adenylate Kinase in Human Health and Disease
Guest Editor: Koichi FujisawaDeadline: 31 January 2024
Special Issue in
IJMS
Neuroinflammation in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias
Guest Editor: Amal KaddoumiDeadline: 15 February 2024
Special Issue in
IJMS
Future Trends in Biomaterials and Devices for Cells and Tissues
Guest Editors: Loredana De Bartolo, Antonella Piscioneri, Seeram RamakrishnaDeadline: 27 February 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
IJMS
Feature Papers in Bioactives and Nutraceuticals
Collection Editor: Maurizio Battino
Topical Collection in
IJMS
State-of-the-Art Molecular Microbiology in Poland
Collection Editors: Alicja Wegrzyn, Satish Raina
Topical Collection in
IJMS
Computational, Structural and Spectroscopic Studies of Enzyme Mechanisms, Inhibition and Dynamics
Collection Editor: Christo Christov










