-
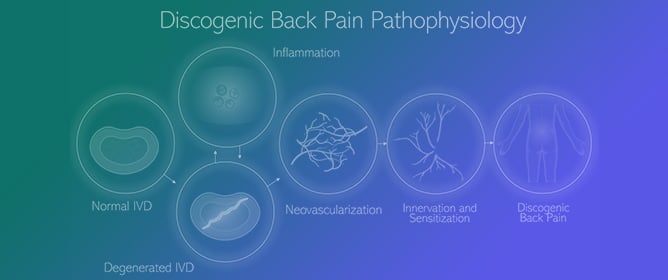 Updates on Pathophysiology of Discogenic Back Pain
Updates on Pathophysiology of Discogenic Back Pain -
 Autoimmune Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia
Autoimmune Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia -
 Oral Manifestations of Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Oral Manifestations of Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review -
 Therapeutic Use of Low-Dose Local Anesthetics in Pain, Inflammation, and Other Clinical Conditions: A Systematic Scoping Review
Therapeutic Use of Low-Dose Local Anesthetics in Pain, Inflammation, and Other Clinical Conditions: A Systematic Scoping Review -
 Diaphragmatic Endometriosis—A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of the Patients’ Demographics, Symptomatology, and Long-Term Treatment Outcomes
Diaphragmatic Endometriosis—A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of the Patients’ Demographics, Symptomatology, and Long-Term Treatment Outcomes
Journal Description
Journal of Clinical Medicine
Journal of Clinical Medicine
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of clinical medicine, published semimonthly online by MDPI. The International Bone Research Association (IBRA), Italian Resuscitation Council (IRC), Spanish Society of Hematology and Hemotherapy (SEHH), Japan Association for Clinical Engineers (JACE), European Independent Foundation in Angiology/ Vascular Medicine (VAS) and others are all affiliated with JCM, and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Medicine, General & Internal) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for JCM include: Epidemiologia, Transplantology, Uro, Sinusitis, Rheumato, Biologics, Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology, Journal of Vascular Diseases, Osteology, and Complications.
Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.1 (2022)
Latest Articles
Association of Fat Mass and Skeletal Muscle Mass with Cardiometabolic Risk Varied in Distinct PCOS Subtypes: A Propensity Score-Matched Case-Control Study
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 483; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020483 (registering DOI) - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
(1) Background: polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a heterogeneous syndrome with a constellation of cardiometabolic risk factors. We aimed to investigate if the association of body fat mass (BFM) and skeletal muscle mass (SMM) with cardiometabolic risk differed in PCOS subtypes. (2) Methods:
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a heterogeneous syndrome with a constellation of cardiometabolic risk factors. We aimed to investigate if the association of body fat mass (BFM) and skeletal muscle mass (SMM) with cardiometabolic risk differed in PCOS subtypes. (2) Methods: 401 participants (245 PCOS and 156 controls) were assessed for anthropometric measurements, glucose–lipid profiles, reproductive hormones and body composition with propensity score-matched (PSM) analysis. The association of the cardiometabolic risk score (z score, calculated based on levels of obesity and gluco-lipid measurements) with BFM (estimated by trunk BFM/Height2) and SMM (estimated by SMM/Height2) was calculated. (3) Results: Trunk BFM/Height2 and SMM/Height2 were both positively associated with cardiometabolic risk in PCOS (trunk BFM/Height2, OR 2.33, 95% CI 1.49–3.65; SMM/Height2, OR 2.05, 95% CI 1.12–3.76). SMM/Height2 associated with increased cardiometabolic risk in obese PCOS (BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2, OR 2.27, 95% CI 1.15–4.47). For those with lower BMI (<28 kg/m2), trunk BFM/Height2 showed a higher OR in both groups (PCOS, OR 2.12, 95% CI 1.06–4.24; control 2.04, 95% CI 1.04–4.02). Moreover, distinct associations among BMI-stratified groups were validated in hierarchical clustering identifying metabolic and reproductive clusters. (4) Conclusions: BFM and SMM are synergistically associated with higher cardiometabolic risk in PCOS women. Although BFM contributes to increased cardiometabolic risk, SMM also plays a primary role in obese PCOS. Our results highlight the importance of body composition in the management of PCOS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Inappropriate Body Composition in Patients with Diabetes)
Open AccessArticle
Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Patients with Chronic Whiplash-Associated Disorders: Differences between Subgroups Based on the Central Sensitization Inventory
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 482; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020482 (registering DOI) - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Background: Physical exercise is an important element in the rehabilitation of chronic whiplash-associated disorders, with the physiological process underlying pain reduction called exercise-induced hypoalgesia. In chronic whiplash-associated disorders, exercise-induced hypoalgesia appears impaired, and the research suggests a relationship with symptoms of dysfunctional nociceptive
[...] Read more.
Background: Physical exercise is an important element in the rehabilitation of chronic whiplash-associated disorders, with the physiological process underlying pain reduction called exercise-induced hypoalgesia. In chronic whiplash-associated disorders, exercise-induced hypoalgesia appears impaired, and the research suggests a relationship with symptoms of dysfunctional nociceptive processing, such as central sensitization. This study improves our understanding of exercise-induced hypoalgesia in chronic whiplash-associated disorders by examining the differences between the extent of exercise-induced hypoalgesia in subgroups based on scores on the central sensitization inventory (CSI). Methods: Data were collected from 135 participants with chronic whiplash-associated disorders who completed a set of questionnaires. Pain pressure thresholds and temporal summations were assessed before and after a submaximal aerobic bicycle exercise test. Results: We observed no interaction effect between exercise-induced hypoalgesia and the CSI scores for both pain pressure threshold and temporal summation. No overall statistical effect was measured in the analysis of the effect of time. The pain pressure threshold significantly related to the CSI. The temporal summation showed no correlation. Conclusions: During this study, we did not find evidence for a difference in the presence of exercise-induced hypoalgesia when the subgroups were created based on the central sensitization cluster calculator. Limited evidence was found for the influence of CSI scores on the delta pain pressure threshold.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Rehabilitation and Management of Chronic Pain)
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Vildagliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, on the Parameters of Glucose Metabolism and the Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
by
, , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 481; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020481 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
DPP-4 inhibitors are frequently used as first-line agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in Japan. This study aimed to examine the effects of vildagliptin on glucose metabolism and arterial stiffness. Twenty treatment-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes (8 males and 12
[...] Read more.
DPP-4 inhibitors are frequently used as first-line agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in Japan. This study aimed to examine the effects of vildagliptin on glucose metabolism and arterial stiffness. Twenty treatment-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes (8 males and 12 females) received vildagliptin 50 mg twice daily for 6 months. Self-monitored blood glucose measurements and a 75 g OGTT were performed. Arterial stiffness was assessed using the CAVI. After the vildagliptin treatment, a significant decrease in the median HbA1c (from 8.3 to 6.4%) and fasting HOMA-β (from 26.1 to 34.5%), and a marginally significant decrease in the CAVI (from 8.9 to 8.4, p = 0.087) were observed. The glycemic variability parameters also improved, whereas the insulin sensitivity and oxidative stress remained unchanged. Participants with a lower glycemic variability on the 75 g OGTT after vildagliptin treatment showed a significant decrease in their CAVI. The baseline BMI was significantly higher for the participants with a decreased CAVI than in those with no change in their CAVI (24.5 vs. 20.8 kg/m2). After vildagliptin treatment, a decrease in the CAVI was observed, especially in the individuals with improved glycemic variability on the 75 g OGTT. Vildagliptin may be suitable for vascular protection in individuals with high glycemic variability and/or an elevated BMI.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insights into Arterial Stiffness)
►▼
Show Figures
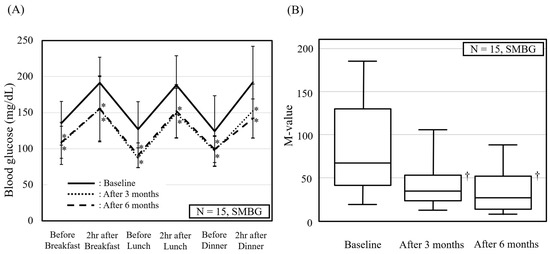
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Early-Staged Carotid Artery Stenting Prior to Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Analysis of the Early and Mid-Term Results in Comparison with a Consecutive Cohort of Isolated Coronary Artery Surgery Patients
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 480; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020480 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Aim: The aim of the present study was to analyze retrospectively the results of patients who underwent early-staged, i.e., within 24–48 h, carotid artery stenting (e-s CAS) before coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Methods: Between December 2014 and December 2022, 1046 consecutive patients
[...] Read more.
Aim: The aim of the present study was to analyze retrospectively the results of patients who underwent early-staged, i.e., within 24–48 h, carotid artery stenting (e-s CAS) before coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Methods: Between December 2014 and December 2022, 1046 consecutive patients underwent CABG; 31 of these patients (3%) were subjected to e-s CAS prior to CABG (e-s CAS + CABG group). Preoperative and intraoperative variables and early and mid-term results of the e-s CAS + CABG group were compared with those of patients who underwent isolated CABG (CABG group). Results: As compared with the CABG group, the e-s CAS + CABG group showed a worse clinical risk profile due to higher Euroscore-2 values and incidence of obstructive pulmonary disease and bilateral carotid artery and peripheral artery diseases (p < 0.05, for all comparisons). The combined end point of operative mortality, periprocedural myocardial infarction, and stroke was 3.2% (0% /0% /3.2%) in the e-s CAS + CABG group vs. 5.9% (2.2% /2.8% /0.9%) in the CABG group (p > 0.5, for all measurements). At 5 years, actuarial survival was 74% ± 16% in the e-s CAS + CABG group vs. 93% ± 4.0% in the CABG group, freedom from cardiac death was 100% vs. 98% ± 1.0% (p = 0.6), and freedom from MACCEs was 85% ± 15% vs. 97% ± 2.5% (p > 0.1, for all comparisons). Independent predictors of all-causes death were advanced age at the operation (p < 0.0001), a lower value for left ventricular ejection fraction (p = 0.05), and a high Euroscore-2 (p = 0.04). Conclusions: CABG preceded by e-s CAS appears to be associated with satisfactory early outcomes while limiting the risk of myocardial infarction to a very short time interval between the two procedures. Freedom from late all-causes death, cardiac death, and MACCEs were comparable and equally satisfactory, underscoring the positive protective effects of CAS and CABG on the carotid and coronary territories over time.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Medicine)
Open AccessArticle
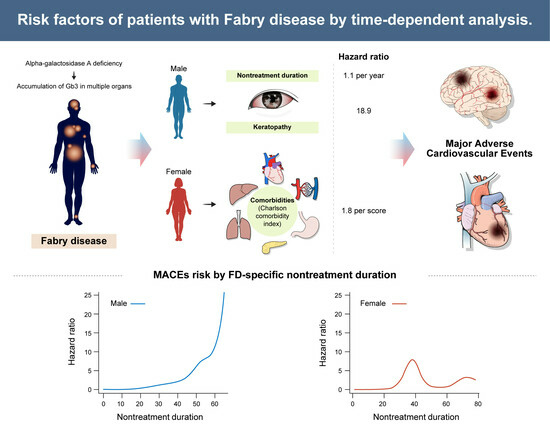
Impact of Nontreatment Duration and Keratopathy on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Fabry Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 479; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020479 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Fabry disease (FD) is a rare inherited X-linked lysosomal storage disorder that results in the progressive accumulation of glycosphingolipids in multiple organs. Early FD-specific treatments may improve clinical outcomes; however, clinical evidence about early FD treatment is limited. We aimed to determine the
[...] Read more.
Fabry disease (FD) is a rare inherited X-linked lysosomal storage disorder that results in the progressive accumulation of glycosphingolipids in multiple organs. Early FD-specific treatments may improve clinical outcomes; however, clinical evidence about early FD treatment is limited. We aimed to determine the cardiovascular outcomes of patients with FD who received enzyme replacement therapy. This nationwide observational study was conducted using the National Health Claims database of the Korean population with FD. The primary outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs). MACE risk factors in FD were evaluated using time-dependent Cox regression. Between January 2007 and April 2022, 188 patients with FD were analyzed. Among them, 22 (11.7%) experienced MACE (males: 14/95 [14.7%]; females: 8/93 [8.6%]). The mean age at MACE diagnosis was 53.5 ± 11.0 years in all patients with FD, which was lower in males compared with in females (49.7 ± 9.6 vs. 60.0 ± 10.7 years, p = 0.030). Multivariate analysis (HR, 95% CI) revealed that age (1.042; 1.004–1.082) and duration of FD nontreatment (1.040; 1.003–1.078) were significant MACE risk factors in all patients. In males, age (1.080; 1.032–1.131), FD nontreatment duration (1.099; 1.048–1.152), and keratopathy (18.920; 4.174–85.749) were significant MACE risk factors in multivariate analysis. In females, the only significant MACE risk factor was a high Charlson comorbidity index score (1.795; 1.229–2.622). In conclusion, duration of FD nontreatment and keratopathy are significant MACE risk factors in males with FD. These findings suggest the importance of early initiation of FD-specific treatment and careful evaluation of keratopathy in males with FD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Is Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma a Vascular Disease? Assessment of the Relationship between Retinal Arteriolar Morphology and Glaucoma Severity Using Adaptive Optics
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 478; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020478 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Background: Retinal vascular abnormalities may be associated with glaucomatous damage. Adaptive optics (AO) is a new technology that enables the analysis of retinal vasculature at the cellular level in vivo. The purpose of this study was to evaluate retinal arteriolar parameters using the
[...] Read more.
Background: Retinal vascular abnormalities may be associated with glaucomatous damage. Adaptive optics (AO) is a new technology that enables the analysis of retinal vasculature at the cellular level in vivo. The purpose of this study was to evaluate retinal arteriolar parameters using the rtx1 adaptive optics fundus camera (AO-FC) in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) at different stages and to investigate the relationship between these parameters and changes in spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) and perimetry. Methods: Parameters of the retinal supratemporal and infratemporal arterioles (wall thickness (WT), lumen diameter (LD), total diameter (TD), wall-to-lumen ratio (WLR), and cross-sectional area of the vascular wall (WCSA)) were analysed with the rtx1 in 111 POAG eyes, which were divided into three groups according to the severity of the disease, and 70 healthy eyes. The associations between RTX1 values and the cup-to-disk ratio, SD-OCT parameters, and visual field parameters were assessed. Results: Compared with the control group, the POAG groups showed significantly smaller TD and LD values (p < 0.05) and significantly higher WLR and WT values (p < 0.05) for the supratemporal and infratemporal arterioles. TD was significantly positively correlated with the retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) and ganglion cell complex (GCC) (p < 0.05). LD was significantly positively correlated with the RNFL, GCC, and rim area (p < 0.05). The WLR was significantly negatively correlated with the RNFL, GCC, rim area, and MD (p < 0.05), while it was significantly positively correlated with the cup-to-disc ratio and PSD (p < 0.05). Conclusions: The results suggest that vascular dysfunction is present in POAG, even at a very early stage of glaucoma, and increases with the severity of the disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Clinical Treatment for Ocular Vascular Disease and Fundus Disease)
►▼
Show Figures
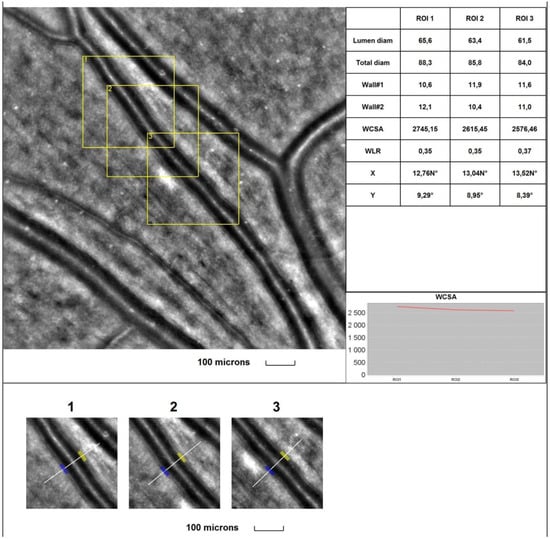
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
The Occurrence of Atopy in Patients with Isolated Spontaneous Mast Cell (or Nonallergic) Angioedema
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 477; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020477 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Background: Isolated mast cell angioedema (MC-AE) can be divided into allergic and nonallergic (spontaneous) forms. The former is often associated with food, Hymenoptera venoms or drug allergies. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the occurrence of atopic diseases and the risk
[...] Read more.
Background: Isolated mast cell angioedema (MC-AE) can be divided into allergic and nonallergic (spontaneous) forms. The former is often associated with food, Hymenoptera venoms or drug allergies. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the occurrence of atopic diseases and the risk of angioedema. Methods: A retrospective study analyzed 304 patients with confirmed MC-AE and 1066 controls. All were analyzed for allergic asthma (AA), atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic rhinitis (AR) based on ICD-10 codes. In addition, total IgE and peripheral eosinophilia were calculated. Results: The analyzed atopic diseases were more frequent in the group of patients diagnosed with MC-AE than in the controls: 78 (25.7%) vs. 173 (16.2%) for p < 0.01. Patients diagnosed with AD had a higher risk of MC-AE (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.48,) similar to those diagnosed with AR (HR = 1.51). However, in patients with two or three atopic comorbidities, the risk increased significantly to HR = 2.45 or HR = 4.1, respectively. There was a positive correlation between the serum total IgE concentration or eosinophilia and the risk of angioedema (p < 0.01). Conclusion: Patients with MC-AE had a more frequent occurrence of atopic diseases associated with inhalant allergies. This risk increased in patients with IgE-mediated polymorphic disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Allergic and Eosinophilic Diseases: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
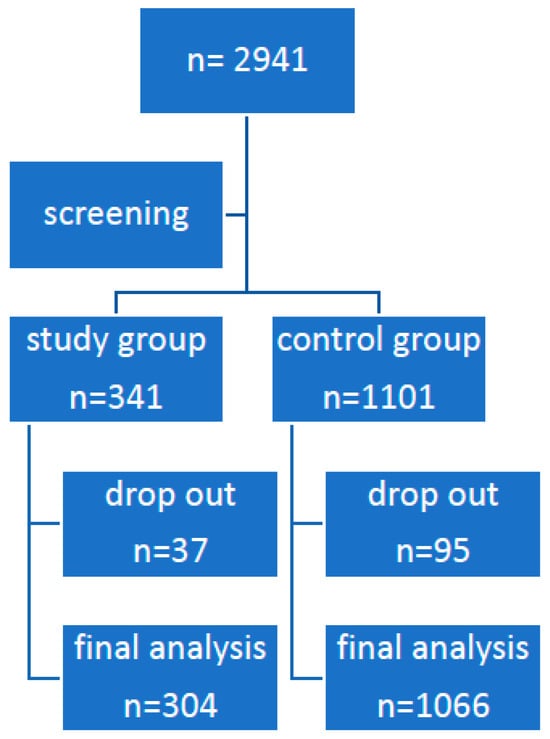
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Trends in the Incidence of Cardiovascular Diagnoses and Procedures over the Years 2012–2021 in Israel: The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
, , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 476; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020476 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Prior studies found reduced incidences of cardiovascular diagnoses and treatments in the initial phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, these studies included a limited number of outcomes and did not consider pre-pandemic trends. This study aimed to describe trends in the incidence of
[...] Read more.
Prior studies found reduced incidences of cardiovascular diagnoses and treatments in the initial phase of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, these studies included a limited number of outcomes and did not consider pre-pandemic trends. This study aimed to describe trends in the incidence of cardiovascular diagnoses and treatments over the years 2012–2021 in Israel and to compare the two years of the COVID-19 period with the preceding 8 years. In this retrospective, population-based study, carried out within Clalit Health Services, the incidence rates of cardiovascular outcomes were calculated for individuals aged ≥ 25 (~2.7 million adults per year) during the first (Y1, 3/2020–2/2021) and second (Y2, 3/2021–2/2022) years of COVID-19 and the 8 years prior (3/2012–2/2020). Declines were observed in Y1 compared to 2019 in all diagnoses and treatments: STEMI (−16.3%; 95% CI: −16.6, −16.1), non-STEMI (−16.4%; −16.6, −16.2), AF (−14.1%; −14.2, −14.0), CHF (−7.8%; −7.9, −7.7), CVA (−5.0%; −5.0, −4.9), catheterization (−64.7%; −65.2, −64.2), CABG (−77.7%; −79.2, −76.2), ablation (−21.2%; −22.0, −20.4), pacemaker implantation (−39.3%; −40.7, −37.9), and defibrillator insertion (−12.5%; −13.1, −12.0). Compared with expected rates based on pre-pandemic trends, observed rates were within expected ranges (CHF, CVA, and ablation), less than expected (STEMI, non-STEMI, AF, catheterization, CABG, and pacemaker insertion), or more than expected (defibrillator insertion). In Y2, STEMI, catheterization, and CABG returned to expected rates; non-STEMI and AF were lower than expected; and CHF, CVA, ablation, and pacemaker and defibrillator implantations were higher than expected. Several cardiovascular diagnoses and treatment trends were interrupted by COVID-19. The long-term consequences of these changes should be considered by health policymakers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
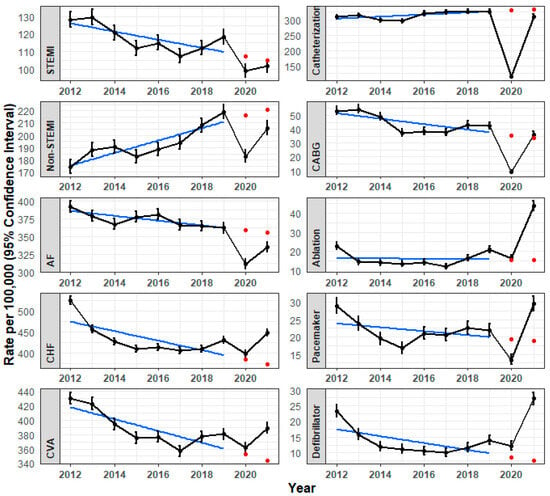
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Efficacy of Core-Strengthening and Intensive Dynamic Back Exercises on Pain, Core Muscle Endurance, and Functional Disability in Patients with Chronic Non-Specific Low Back Pain: A Randomized Comparative Study
by
, , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 475; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020475 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Background: Chronic back pains are progressively disabling working individuals, including 60–80% of the general population, for which their diagnosis is challenging to healthcare workers worldwide, thereby becoming a burden to nations. Purpose: The study aimed to investigate the efficacy of core strengthening exercise
[...] Read more.
Background: Chronic back pains are progressively disabling working individuals, including 60–80% of the general population, for which their diagnosis is challenging to healthcare workers worldwide, thereby becoming a burden to nations. Purpose: The study aimed to investigate the efficacy of core strengthening exercise (CSE) and intensive dynamic back exercise (IDBE) on pain, core muscle endurance, and functional disability in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain (LBP). Methods: The study was based on a three-arm parallel-group randomized control design. Forty-five participants with chronic non-specific LBP were recruited and randomly divided into the CSE, IDBE, and Control groups. The CSE and IDBE groups received CSE and IDBE, respectively. However, the Control group received no intervention. Numeric pain rating scale, Oswestry Disability Index, core flexors, extensors, and side bridge tests assessed pain intensity, functional disability, and endurance of core muscles. Outcome scores for the dependent variables were collected at baseline (pre-intervention) and six-week post-intervention. There were no follow-up measurements in this study. A one-way multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA) was used to analyze the intervention effects on the outcomes within groups and between groups, respectively; keeping the significance-level alpha at 95%, i.e., p < 0.05. A univariate F-test was performed to observe the superiority of one treatment over another. Pearson’s correlation coefficient test was conducted to determine a relation between the dependent variables. In all statistical analyses, the level of significance α was kept at 0.05. Results: All forty-five out of sixty-three participants with chronic non-specific low back pain (male, 32 and female, 23; average age, 20.24 ± 1.46 years; average pain duration, 19.6 ± 5.42 weeks) completed the study and their data were analyzed. The MANCOVA test showed a significant difference between the treatment groups on the combined multiple endurance tests for the core muscles (flexors, extensors, side bridge tests to the right and left), Visual Analog Scale (VAS), and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) scores after controlling for baseline scores of all the dependent variables: F (6, 12) = 23.381; p < 0.05; Wilks’ Λ = 0.033; partial η2 = 0.819. A post hoc pair-wise comparison followed by a univariate F-test indicated that a significant improvement was found between the CSE vs. IDBE vs. Control groups on the post-test scores of all the dependent variables except VAS and EET (CSE vs. IDBE only). A Pearson’s correlation coefficient test revealed a notable relation between the dependent variables. Conclusions: The experimental group CSE was found to be more effective than IDBE on improving functional disability, cores’ flexors, and side bridges’ endurance tests than IDBE. The magnitude of this improvement exceeded the minimal clinically important difference (MCID), suggesting a clinically relevant enhancement in functional disability, core flexors, and side bridge endurance for participants engaged in CSE. However, CSE vs. IDBE revealed non-significant differences on reducing pain and core extensors’ endurance. The absence of statistically significant differences suggests that the observed changes did not exceed the established MCID for pain intensity and core extensors’ endurance. In addition, partial eta-squared value revealed the superiority of CSE over IDBE and Control groups. This suggests that the observed differences between the two interventions are not only statistically significant, but also clinically relevant, surpassing the established MCID.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Rehabilitation)
►▼
Show Figures
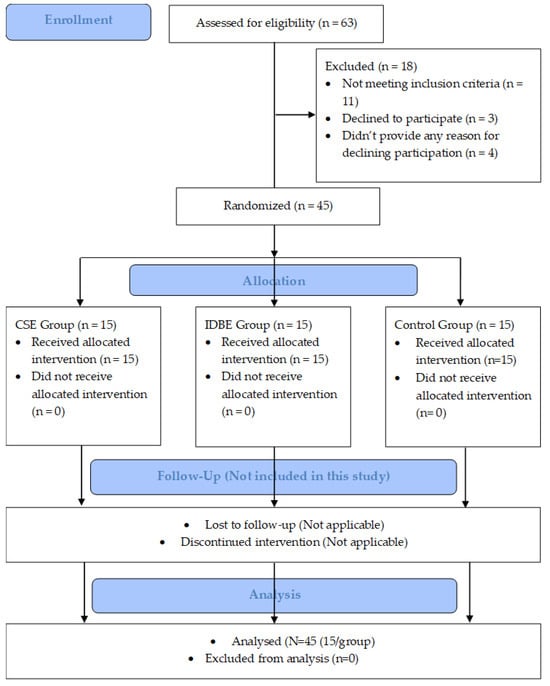
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Using Three-Dimensional Printing Technology to Solve Complex Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Cases: Do We Really Need Custom-Made Guides and Templates? A Critical Systematic Review on the Available Evidence
by
, , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 474; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020474 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The burden of osteoarthritis (OA) is around 300 million people affected worldwide, with the hip representing a commonly affected joint. Total hip arthroplasty (THA) has been used with notable success as a definitive treatment to improve pain and function in hip OA patients.
[...] Read more.
The burden of osteoarthritis (OA) is around 300 million people affected worldwide, with the hip representing a commonly affected joint. Total hip arthroplasty (THA) has been used with notable success as a definitive treatment to improve pain and function in hip OA patients. The recent advent of new technologies, such as 3D printing, has pushed the application of these new concepts toward applications for the well-known THA. Currently, the evidence on the use of 3D printing to aid complex primary THA cases is still scarce. Methods: An extensive literature review was conducted to retrieve all articles centered on the use of 3D printing in the setting of primary THA. Results: A total of seven studies were included in the present systematic review. Four studies investigated the use of 3D-printed surgical guides to be used during surgery. The remaining three studies investigated the benefit of the use of 3D-printed templates of the pelvis to simulate the surgery. Conclusions: The use of 3D printing could be a promising aid to solve difficult primary total hip arthroplasty cases. However, the general enthusiasm in the field is not supported by high-quality studies, hence preventing us from currently recommending its application in everyday practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Orthopedics)
►▼
Show Figures
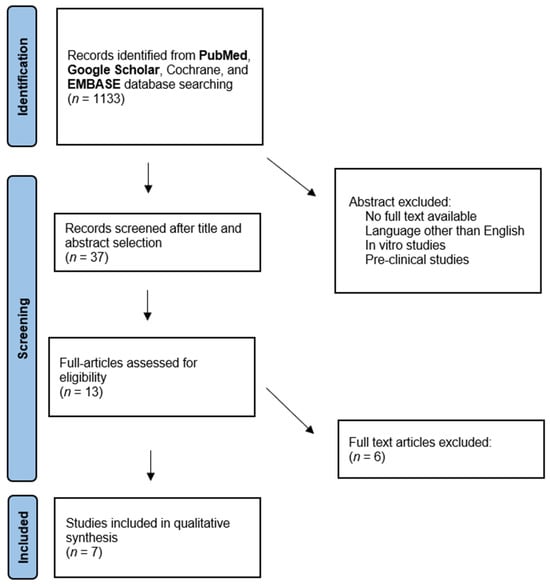
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Mechanical Circulatory Support Strategies in Takotsubo Syndrome with Cardiogenic Shock: A Systematic Review
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 473; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020473 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Background: Takotsubo syndrome is, by definition, a reversible form of acute heart failure. If cardiac output is severely reduced, Takotsubo syndrome can cause cardiogenic shock, and mechanical circulatory support can serve as a bridge to recovery. To date, there are no recommendations on
[...] Read more.
Background: Takotsubo syndrome is, by definition, a reversible form of acute heart failure. If cardiac output is severely reduced, Takotsubo syndrome can cause cardiogenic shock, and mechanical circulatory support can serve as a bridge to recovery. To date, there are no recommendations on when to use mechanical circulatory support and on which device is particularly effective in this context. Our aim was to determine the best treatment strategy. Methods: A systematic literature research and analysis of individual patient data was performed in MEDLINE/PubMed according to PRISMA guidelines. Our research considered original works published until 31 July 2023. Results: A total of 93 publications that met the inclusion criteria were identified, providing individual data from 124 patients. Of these, 62 (50%) were treated with veno-arterial extracorporeal life support (va-ECLS), and 44 (35.5%) received a microaxial left ventricular assist device (Impella). Eighteen patients received an Impella CP and twenty-one an Impella 2.5. An intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) without other devices was used in only 13 patients (10.5%), while other devices (BiVAD or Tandem Heart) were used in 5 patients (4%). The median initial left ventricular ejection fraction was 20%, with no difference between the four device groups except for the IABP group, which was less affected by cardiac output failure (p = 0.015). The overall survival was 86.3%. Compared to the other groups, the time to cardiac recovery was shorter with Impella (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Though the Impella treatment is new, our analysis may show a significant benefit of Impella compared to other MCS strategies for cardiogenic shock in Takotsubo syndrome.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
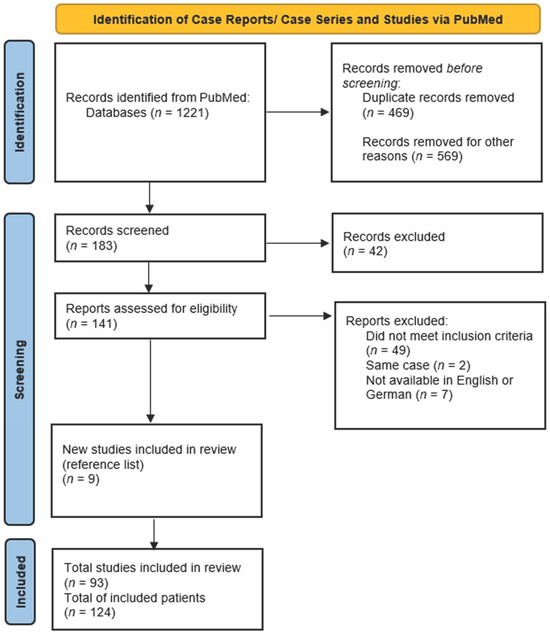
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
A Systematic Review of the Pulmonary Microbiome in Patients with Acute Exacerbation COPD Requiring ICU Admission
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 472; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020472 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major health concern. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) may require intensive care unit (ICU) admission and mechanical ventilation. Acute infections and chronic colonization of the respiratory system are known to precipitate AECOPD. Detailed knowledge of the
[...] Read more.
Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major health concern. Acute exacerbations (AECOPD) may require intensive care unit (ICU) admission and mechanical ventilation. Acute infections and chronic colonization of the respiratory system are known to precipitate AECOPD. Detailed knowledge of the respiratory microbiome could lead to effective treatment and prevention of exacerbations. Objective: The aim of this review is to summarize the available evidence on the respiratory microbiome of patients with a severe AECOPD requiring mechanical ventilation and intensive care admission. Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted to identify the published papers until January 2023. The collected data were then subjected to qualitative analysis. After the first analysis, a secondary focused review of the most recent publications studying the relationship between microbiome and mortality in AECOPD was performed. Results: Out of 120 screened articles six articles were included in this review. Potentially pathogenic microorganisms (PPMs) were identified in 30% to 72% of the patients with community-acquired bacteria, gram-negative enteric bacilli, Stenotrophomonas and Pseudomonas being the most frequently isolated. During hospitalization, 21% of patients experienced colonization by PPMs. Adequate antimicrobial therapy resulted in the eradication of 77% of the identified PPMs. However, 24% of the bacteria displayed multi-drug resistance leading to prolonged or failure of eradication. Conclusion: PPMs are prevalent in a significant proportion of patients experiencing an AECOPD. The most identified PPMs include community-acquired pathogens and gram-negative enteric bacilli. Notably, no differences in mortality or duration of ventilation were observed between patients with and without isolated PPMs. However, the included studies did not investigate the virome of the patients, which may influence the microbiome and the outcome of infection. Therefore, further research is essential to comprehensively investigate the complete microbial and viral composition of the lower respiratory system in COPD patients admitted to the ICU.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Intensive Care)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement as a bridge to minimally invasive endoscopic mitral valve surgery in Elderly Patients in the era of ERAS and Fast Track TAVI concepts
by
, , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 471; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020471 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
In this bicentric study, we report the outcomes of combined transcatheter aortic valve replacement combined with minimally invasive mitral valve surgery. We included a cohort of six patients (79.6 ± 3.2 years, 83% women) with high-risk profiles and deemed to be non-operable with
[...] Read more.
In this bicentric study, we report the outcomes of combined transcatheter aortic valve replacement combined with minimally invasive mitral valve surgery. We included a cohort of six patients (79.6 ± 3.2 years, 83% women) with high-risk profiles and deemed to be non-operable with combined mitral and aortic valvular disease. All patients had unsuitable anatomies for transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair (TEER). Moreover, most of the patients (5/6) suffered a combined aortic valve lesion, which complicates the efficiency of cardioplegia in the case of CBP through minimally invasive incisions. The first stage was implanting a TAVI valve to achieve aortic valve competency and hence facilitate the infusion of cardioplegia after clamping the aorta during endoscopic mitral valve surgery. After one week, we performed the minimally invasive mitral valve repair. Most patients (n = 5; 83%) underwent successful endoscopic mitral valve repair. Intraoperatively, the mean ischemic time was 42 min, and the total bypass time was 72 min. Postoperatively, the mean intubation time was 0 h. Postoperative complications included reoperation for bleeding in one patient (16.7%) and a new heart block requiring pacemaker implantation in one patient (16.7%). There was neither in-hospital mortality nor 1-year mortality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
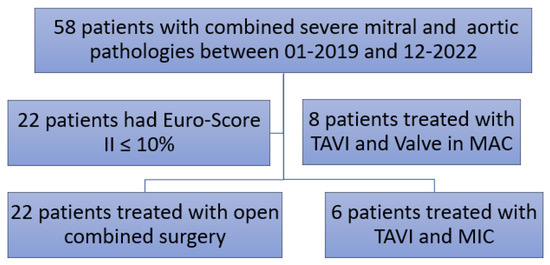
Figure A1
Open AccessCase Report
Endoscopic Vacuum-Assisted Closure (E-VAC) in Septic Shock from Perforated Duodenal Ulcers with Abscess Formations
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 470; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020470 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
This case report underscores the importance of utilizing E-VAC (endoscopic vacuum-assisted closure) in the treatment of a perforated duodenal ulcer complicated by the formation of a subphrenic abscess and septic shock. It showcases how E-VAC can effectively mitigate the risk of further complications,
[...] Read more.
This case report underscores the importance of utilizing E-VAC (endoscopic vacuum-assisted closure) in the treatment of a perforated duodenal ulcer complicated by the formation of a subphrenic abscess and septic shock. It showcases how E-VAC can effectively mitigate the risk of further complications, such as leakage, bleeding, or rupture, which are more commonly associated with traditional methods like stents, clips, or sutures. As a result, there is a significant reduction in mortality rates. A perforated duodenal ulcer accompanied by abscess formation represents a critical medical condition that demands prompt surgical intervention. The choice of the method for abscess drainage and perforation closure plays a pivotal role in determining the patient’s chances of survival. Notably, in patients with a high ASA (American Association of Anesthesiologists) score of IV-V, the mortality rate following conventional surgical intervention is considerably elevated. The management of perforated duodenal ulcers has evolved from open abdominal surgical procedures, which were associated with high mortality rates and risk of suture repair leakage, to minimally invasive techniques like laparoscopy and ingestible robots. Previously, complications arising from peptic ulcers, such as perforations, leaks, and fistulas, were primarily addressed through surgical and conservative treatments. However, over the past two decades, the medical community has shifted towards employing endoscopic closure techniques, including stents, clips, and E-VAC. E-VAC, in particular, has shown promising outcomes by promoting rapid and consistent healing. This case report presents the clinical scenario of a patient diagnosed with septic shock due to a perforated duodenal ulcer with abscess formation. Following an exploratory laparotomy that confirmed the presence of a subphrenic abscess, three drainage tubes were utilized to evacuate it. Subsequently, E-VAC therapy was initiated, with the kit being replaced three times during the recovery period. The patient exhibited favorable progress, including weight gain, and was ultimately discharged as fully recovered. In the treatment of patients with duodenal perforated ulcers and associated abscess formation, the successful and comprehensive drainage of the abscess, coupled with the closure of the perforation, emerges as a pivotal factor influencing the patient’s healing process. The positive outcomes observed in these patients underscore the efficacy of employing a negative pressure E-VAC kit, resulting in thorough drainage, rapid patient recovery, and low mortality rates.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Minimally Invasive Surgery: Current Challenges and New Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures
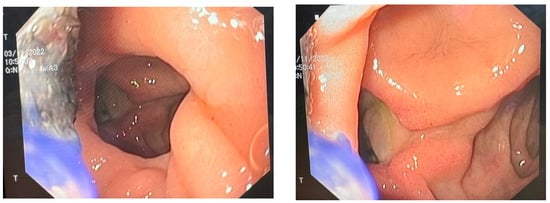
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Respiratory Failure on Peripheral and Organ Perfusion Markers in Severe COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study
by
, , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 469; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020469 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Microvascular dysfunction and inflammation caused by COVID-19 disrupt organ function. The study aimed to investigate the association between the severity of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia and peripheral and organ perfusion as a consequence of altered microcirculation. A total of 116 patients hospitalized due to severe
[...] Read more.
Microvascular dysfunction and inflammation caused by COVID-19 disrupt organ function. The study aimed to investigate the association between the severity of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia and peripheral and organ perfusion as a consequence of altered microcirculation. A total of 116 patients hospitalized due to severe COVID-19 were enrolled in the study. On admission, the patients underwent a Capillary Refill Time (CRT) examination, finger oxygen saturation measurement, thermal imaging of the hand (FIT), and a kidney Doppler ultrasound. Medical data were collected from the medical history. From the evaluated perfusion parameters, only renal cortex perfusion (RCP) was substantially correlated with the CT score (p < 0.010). The peripheral perfusion parameters of Sat., FIT, CRT, and RCP correlated with the ARDS stages (p = 0.0021; p = 0.038; p < 0.0006; p < 0.0002, respectively). The Oxygenation Ratio value (p < 0.001) was significantly associated with all the perfusion parameters (saturation, CRT, FIT, and RCP) in the multivariable regression analysis model. According to the stepwise retrograde regression analysis, RCP was an independent parameter linked with the Oxygenation Ratio (p < 0.001). Severe COVID-19 can result in microvascular dysfunction influencing peripheral and organ perfusion, which can be measured with various methods. The staging of COVID-19 assessed by CT and the Oxygenation Ratio correlates with RCP, CRT, FIT, and oxygen saturation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
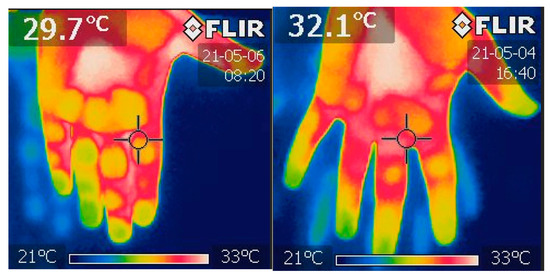
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Extracellular DNA and Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Saliva from Patients with Periodontitis—A Case–Control Study
by
, , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 468; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020468 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease. We have previously shown that salivary DNA is higher in patients with periodontitis. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are involved in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases. The objective of this case–control study was to compare patients with
[...] Read more.
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease. We have previously shown that salivary DNA is higher in patients with periodontitis. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are involved in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases. The objective of this case–control study was to compare patients with periodontitis and healthy controls regarding the salivary concentrations of extracellular DNA and NET components. Unstimulated saliva samples were collected from 49 patients with periodontitis and 71 controls before an oral examination. Salivary extracellular DNA was isolated and quantified fluorometrically and using PCR. NET-associated markers were assessed using ELISA. We have found significantly higher concentrations of salivary extracellular DNA in samples from periodontitis patients (five-times higher for supernatant and three times for pellet). Our results show that patients also have three-times-higher salivary nucleosomes and NET-associated enzymes—myeloperoxidase and neutrophil elastase (both two-times higher). Neutrophil elastase and salivary DNA in the pellet correlated positively with the pocket depth/clinical attachment level in periodontitis patients (r = 0.31—weak correlation; p = 0.03 and r = 0.41—moderate correlation, p = 0.004). Correlations between salivary extracellular DNA and NET enzymes were positive and significant. Based on our results, the higher salivary extracellular DNA in periodontitis seems to be related to components of NETs, albeit with weak to moderate correlations indicating that NETs are produced in periodontitis and can play a role in its pathogenesis similarly to other inflammatory diseases. Further studies should prove this assumption with potential diagnostic and therapeutic consequences.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Stomatognathic Diseases: State of the Art and Future Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures
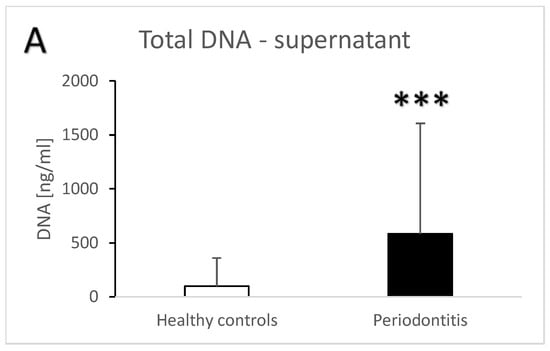
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Does Body Mass Index (BMI) Affect the Reconstruction of Biomechanical Parameters in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Replacement (THR) through the Direct Anterior Approach (DAA)?
by
, , , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 467; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020467 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Objective: Direct anterior approach total hip replacement (DAA-THR) is gaining increased interest due to its tissue-sparing nature and rapid recovery. Obesity has been shown to be a significant parameter influencing cup positioning in DAA-THR. It was the intention of this retrospective study to
[...] Read more.
Objective: Direct anterior approach total hip replacement (DAA-THR) is gaining increased interest due to its tissue-sparing nature and rapid recovery. Obesity has been shown to be a significant parameter influencing cup positioning in DAA-THR. It was the intention of this retrospective study to examine how obesity would influence the restoration of native hip biomechanical parameters during DAA-THR. Materials and Methods: A total of 74 patients from a high-volume university orthopedic center after unilateral DAA-THA were included. Patients were retrospectively allocated to a study group (BMI > 30 kg/m2) and a control group (BMI < 30 kg/m2). Furthermore, propensity-score matching for baseline parameters was performed, leaving 30 patients in each group. Biomechanical parameters of the hip (i.e., femoral offset (FO), abductor lever arm (ABL), acetabular offset (AO), center of rotation (COR), stem alignment (SA), body weight lever arm (BWL), cup inclination (CI), and leg length discrepancy (LLD) were evaluated on standardized plain radiographs, and parameters were compared to the native contralateral hip. Results: Mean BMI in the study group was 35.07 ± 5.13 kg/m2 and 25.43 ± 2.64 kg/m2 in the control group. There was a significant decrease of the ABL only in the study cohort (p = 0.01). CI and SA did not differ between both cohorts. FO was slightly increased compared to the native hip in both groups. There was a marginally higher but non-significant proportion of improper FO restoration in the study group (19 vs. 16 patients, p = 0.60). Conclusions: Obesity, as quantified by BMI, only has a limited impact on the adequate reconstruction of native biomechanical parameters of the hip during DAA-THR. ABL was the only parameter to be significantly decreased in the overweight patients after DAA-THR. Therefore, special care should be taken on proper acetabular reaming and consequent seating of the cup in the obese patient to avoid excessive lateral positioning.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Trends in Hip Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
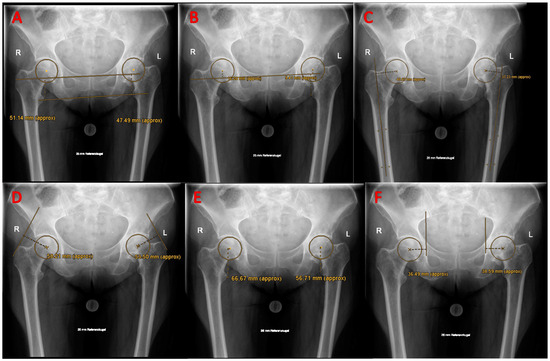
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Fetal and Placental Causes of Elevated Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels in Pregnant Women
by
, , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 466; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020466 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
The most common association related to alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is fetal neural tube defect (NTD), and indeed, this is where the international career of this protein began. In times when ultrasonography was not yet technically advanced, the detection of high levels of AFP in
[...] Read more.
The most common association related to alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is fetal neural tube defect (NTD), and indeed, this is where the international career of this protein began. In times when ultrasonography was not yet technically advanced, the detection of high levels of AFP in maternal serum (MS-AFP) and amniotic fluid was the basis for suspecting neural tube defects. In cases where there was no confirmation of NTD, other causes were sought. It has been established that high titers of MS-AFP could originate in other defects or diseases, such as (1) increased proteinuria in severe fetal kidney diseases; (2) pathological overproduction in liver diseases; (3) penetration through the membranes of gastrointestinal organs exposed to amniotic fluid; (4) passage through the walls of skin vessels; and as a side effect of (5) hepatic hematopoiesis and increased transfer through the edematous placenta in fetal anemia. This article provides a review of the current literature on congenital defects and genetic diseases in the fetus where an elevated level of MS-AFP may serve as the initial diagnostic clue for their detection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Obstetrics & Gynecology)
►▼
Show Figures
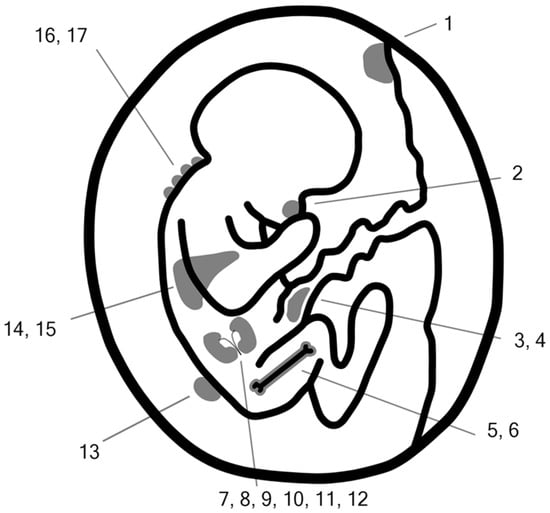
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Glucose Metabolism and Cognitive Decline in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome: A Preliminary Study
by
, , , , , , and
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 465; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020465 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
Multiple studies have analyzed the possible correlations between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Less is known about the context of cognitive deterioration among patients with atypical Parkinsonian syndromes and glucose metabolism impairment. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between the
[...] Read more.
Multiple studies have analyzed the possible correlations between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Less is known about the context of cognitive deterioration among patients with atypical Parkinsonian syndromes and glucose metabolism impairment. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between the impaired glucose metabolism and cognitive decline among patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and corticobasal syndrome (CBS). The study included 22 patients with PSP and CBS with disease durations varying from 3 to 6 years. The levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C), fasting blood glucose, fasting C-peptide and the presence of microalbuminuria were evaluated, and oral glucose tolerance tests (OGTT) were performed. Based on the OGTT results, the glycemic variability, mean glycemia, glycemia standard deviation (SD) and coefficient of variation (%CV) were calculated. All patients underwent a three-Tesla brain magnetic resonance (MRI) examination and neuropsychological cognitive assessment with the use of standardized scales: Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB). A statistical analysis revealed that poor control of glycemia with high glycemic variability and increased atrophy of the medial temporal lobe among patients with PSP and CBS correlated with worse cognitive performance independent of age or sex, even among patients who did not fulfill the criteria for diabetes. The study results indicate the importance of glucose metabolism control and optimal treatment in the context of cognition maintenance among patients with PSP and CBS. Due to the relatively small number of analyzed patients, the issue requires further assessment. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study discussing the role of glycemic variability in atypical Parkinsonian syndromes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Neurology)
►▼
Show Figures
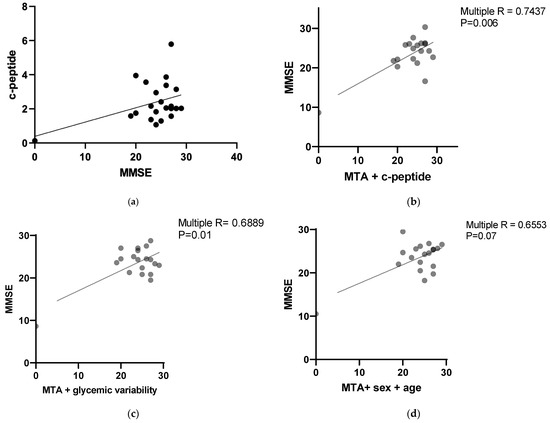
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
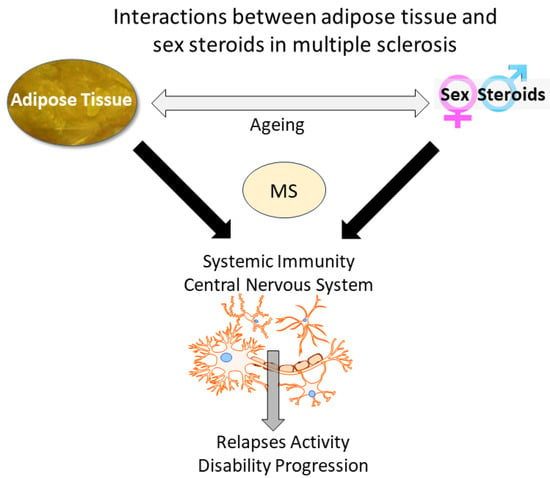
Oral Contraceptives Interact with Adiposity-Associated Markers in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13(2), 464; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020464 - 14 Jan 2024
Abstract
Growing evidence suggests the involvement of adipose tissue in modulating the clinical course of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). This study aimed to investigate whether the intake of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) affects body weight and leptin and adiponectin (APN) blood levels in these
[...] Read more.
Growing evidence suggests the involvement of adipose tissue in modulating the clinical course of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). This study aimed to investigate whether the intake of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) affects body weight and leptin and adiponectin (APN) blood levels in these patients. Clinical data from 62 women (M = 33.23 year) were recorded prior to the initiation of disease-modifying therapy. Patients who were taking COCs at the time of experiencing the first symptoms of disease (COC user) were compared with those who never used these formulations or stopped taking them before disease onset (COC non-user). Bivariate Pearson’s correlations and hierarchical multiple linear regressions analysis were conducted. Normalized APN levels were lower in the COC-using patients (p = 0.013). Negative correlations between waist circumference and normalized APN (p = 0.001) were observed only in the COC non-user patients. A longer duration of COC intake was associated with increased body mass index and waist circumference (p = 0.003). Normalized APN predicted the MS Severity Score (MSSS) (p = 0.020), but this correlation was lost in the COC user patients. After adjusting for confounders, only age (p = 0.027) and, later, disease onset (p = 0.014) were correlated with the MSSS. Larger and prospective studies are needed to investigate the interactions of sex steroids with adipose metabolism in modulating disease progression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Neurology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- JCM Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
10 January 2024
Meet Us at the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research, 18–20 April 2024, Yokohama, Japan
Meet Us at the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research, 18–20 April 2024, Yokohama, Japan

9 January 2024
Meet Us at the 7th Symposium on Primary Breast Cancer in Older Women, 1 March 2024, Nottingham, UK
Meet Us at the 7th Symposium on Primary Breast Cancer in Older Women, 1 March 2024, Nottingham, UK

Topics
Topic in
Healthcare, IJERPH, JCM, JPM, Applied Sciences, Technologies
Smart Healthcare: Technologies and Applications
Topic Editors: Gang Kou, Shuai Ding, Li Luo, Tian Lu, Yogesan KanagasingamDeadline: 20 January 2024
Topic in
Diagnostics, JCDD, JCM, JPM, Medicina
Cardiovascular Disease in 2023: Coronary Syndrome, Heart Failure and Structural Heart Disease
Topic Editors: Saverio Muscoli, Rafael Vidal-PerezDeadline: 31 January 2024
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Cells, Diagnostics, IJMS, JCM, Pathogens, Pathophysiology
Applied Sciences and Technologies for Detection and Therapies of Pathologies in the Neuronal Environment
Topic Editors: Muh-Shi Lin, Hong Jiang, Yu-Yo SunDeadline: 29 February 2024
Topic in
JCM, Healthcare, Diseases, Geriatrics
Clinical Features and Intervention of Patients with Chronic Non-Oncologic Pain
Topic Editors: Ferran Cuenca-Martínez, Josué Fernández-CarneroDeadline: 20 March 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JCM
Myocardial Infarction with Nonobstructive Coronary Arteries (MINOCA): Current Status, Challenges and Future Directions
Guest Editors: Giuseppe Ciliberti, Rocco Montone, Sivabaskari Pasupathy, Carmine PizziDeadline: 20 January 2024
Special Issue in
JCM
Endoscopic and Robotic Colorectal Surgery: Recent Developments and Emerging Trends
Guest Editors: Marco Milone, Michele ManigrassoDeadline: 31 January 2024
Special Issue in
JCM
New Frontiers in Endodontic Dentistry
Guest Editor: Luciano GiardinoDeadline: 5 February 2024
Special Issue in
JCM
Delivery of Anesthesia: Pre-Operative and Post-Operative
Guest Editor: Krzysztof LaudanskiDeadline: 29 February 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
JCM
Clinical Research and Advances in Hemodialysis
Collection Editors: Mariusz Kusztal, Kultigin Turkmen
Topical Collection in
JCM
Cardiovascular Disease: Risk Factors, Comorbidities, and Prevention
Collection Editor: François Roubille
Topical Collection in
JCM
Current Advances and Future Directions for Antithrombotic Treatment Strategies
Collection Editor: Giulio Francesco Romiti
Topical Collection in
JCM
Impact of COVID-19 on the Dental Community
Collection Editors: Hans-Peter Howaldt, Sameh Attia









