Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, peer-reviewed, open-access journal on environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings, published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC), International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) and Urban Land Institute (ULI) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
- Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2022)
Latest Articles
Value Creation with Project Risk Management: A Holistic Framework
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 753; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020753 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The conceptual shift, from a traditional task perspective and a managerial approach to project risks toward a value-centric view, underlines the challenge of creating different forms of value for multiple project stakeholders. This emerging theme arises the need for a new holistic framework
[...] Read more.
The conceptual shift, from a traditional task perspective and a managerial approach to project risks toward a value-centric view, underlines the challenge of creating different forms of value for multiple project stakeholders. This emerging theme arises the need for a new holistic framework for value creation through Project Risk Management (PRM). With this purpose, the paper aims at deepening the knowledge about PRM for value creation. A systematic literature review has been conducted, extracting a database of 116 papers. To address the research questions, a descriptive and a content analysis have been performed. The results of a systematic literature review reveal that the value created through PRM includes both economic and intangible (not monetary) benefits. Moreover, even if international standards are giving greater relevance to value creation and protection, considering also the potential positive effects of risks, empirical results show significant discrepancies. From the analysis of the results, a new theoretical framework emerges that integrates fundamental aspects not fully considered so far, incorporating the concepts of economic, ecological, and social impacts into the notion of value creation through PRM. This work extends the current research in this field and sets forth the definition of a holistic framework to promote the creation of value for project stakeholders in practice, through the management of negative and positive risks, providing a perspective on the sustainability orientation of projects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Using Project Management as a Way to Sustainability)
Open AccessArticle
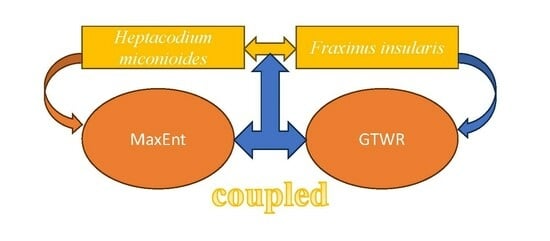
Regional Analysis of the Potential Distribution of Heptacodium miconioides and Its Competitor Species in China
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 752; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020752 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Heptacodium miconioides is listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as a rare and endangered plant which is being subjected to competition for environmental resources by Fraxinus insularis. The impact of competing species on the dispersal of H. miconioides
[...] Read more.
Heptacodium miconioides is listed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as a rare and endangered plant which is being subjected to competition for environmental resources by Fraxinus insularis. The impact of competing species on the dispersal of H. miconioides across time and space is unclear, which hinders our ability to effectively protect rare and endangered species. Therefore, in this study, we performed a spatial analysis of the interactions between H. miconioides and F. insularis using the Maximum Entropy model (MaxEnt) coupled with the Spatio-temporal Geographic Weighted Regression Model. The results show that: Among the 20 environmental factors selected, Precipitation in Driest Quarter (Bio17) was the primary factor affecting H. miconioides and F. insularis. An expansion of H. miconioides and F. insularis habitats will be seen in future environments compared to current environments. Under the current climatic conditions, the ecological niche overlap has a D value of 0.7261 and an I value of 0.9188, and the ecological niche overlap will increase further in future environments. The distribution of F. insularis practically covered the area suitable for H. miconioides, and the influence of F. insularis’s suitability index on H. miconioides gradually increased. The region of negative impacts has changed, with distribution in the current environment in the southern part of Shaanxi, eastern Sichuan, and northern part of Zhejiang, China, moving to the southern part of Henan, and the junction between Zhejiang and Anhui in the 2050s. Sustainability is one of the important goals in global development today, and the conservation of rare and endangered plants is one of the most important elements of sustainable development. It is not only beneficial to the survival and health of human beings, but also helps to promote the sustainable development of ecologies, economies, and societies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainability, Biodiversity and Conservation)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Charting the Path of Technology-Integrated Competence in Industrial Design during the Era of Industry 4.0
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 751; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020751 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The fusion of emerging technologies with industrial design has catalyzed a fundamental shift in the aesthetics, user experiences, and service frameworks of products in the Industry 4.0 era. Simultaneously, this convergence has heightened the demands placed on the technological integration competencies of designers.
[...] Read more.
The fusion of emerging technologies with industrial design has catalyzed a fundamental shift in the aesthetics, user experiences, and service frameworks of products in the Industry 4.0 era. Simultaneously, this convergence has heightened the demands placed on the technological integration competencies of designers. Consequently, there exists a necessity to articulate a precise developmental trajectory for proficiency in industrial design that incorporates these novel technologies. This study initiates with a bibliometric analysis to quantify the scholarly literature relevant to this research domain. Subsequently, leveraging the insights from this analysis, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 15 experts spanning the United States, Europe, South Korea, and China. Our conclusions show the following: (1) Co-word analysis and cluster analysis techniques are applied to identify 80 technologies and four technological clusters that demonstrate strong associations with industrial design in the Industry 4.0 era. (2) Employing coding techniques and thematic analysis, four distinct skill domains emerge for technology-integrated industrial design: Industrial Design Skills, Industrial Design Knowledge, Ethical Considerations in Industrial Design, and Industrial Design Industry Insight. Furthermore, a limitation that affects these competencies is identified. (3) A recommended methodology for assessing these competencies is proposed. This study represented an expansion upon existing industrial design competencies. The empirical data generated herein serves as a valuable resource for practitioners and educators within the field of industrial design. Furthermore, it provides a theoretical groundwork for future models addressing technology-infused industrial design capabilities.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Avocado (Persea americana cv. ‘Hass’) Fruit Mineral Composition at Canopy Level towards Sustainable Quality
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 750; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020750 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Sustaining avocado fruit quality is crucial to maintain customer satisfaction and confidence. Among fruit qualities, mineral nutrient composition is an important contributor to postharvest robustness. Towards better understanding and addressing variability within the plant canopy, ‘Hass’ fruit from across seven orchard blocks were
[...] Read more.
Sustaining avocado fruit quality is crucial to maintain customer satisfaction and confidence. Among fruit qualities, mineral nutrient composition is an important contributor to postharvest robustness. Towards better understanding and addressing variability within the plant canopy, ‘Hass’ fruit from across seven orchard blocks were individually characterised. From five representative trees in each block, five fruit were harvested (one from each of five positions: top (sun-exposed), bottom (shaded), middle (shaded), East (sun-exposed), and West (sun-exposed)). Fruit dry matter was significantly higher (p ≤ 0.001) in fruit from the top, East, and West sun-exposed positions. No significant (p > 0.05) effect of position was discerned for fruit weight at harvest or for either stem end rot (SER) or body rot (BR) incidence at eating soft. Shaded fruit had significantly higher (p ≤ 0.05) [N], [K], [Mg], N:Ca, K:Ca, and K + Mg:Ca in their flesh. Significant negative linear correlations (p ≤ 0.001) were obtained between fruit DM and flesh [N] (r = −0.75), [K] (r = −0.67), and N:Ca (r = −0.57). SER and BR incidence were significantly positively correlated (p ≤ 0.01) with flesh and skin mineral ratios of N:Ca, K:Ca, Mg:Ca, and K + Mg:Ca. Skin and flesh [Ca] were significantly negatively correlated with SER (r = −0.51, p ≤ 0.01) and BR (r = −0.74, p ≤ 0.001) incidences. Soil cation (Ca, Mg, K) availability (%base saturation of cation exchange capacity (CEC)) was not (p > 0.05) correlated with skin or flesh mineral concentrations or ratios. Considered collectively, results suggest that selective harvest of sun-exposed fruit with inherently lower mineral nutrient ratios yields relatively robust fruit. Such fruit lots should better tolerate the rigours of harvest and postharvest treatment and handling. In this context, they should better maintain quality upon passage through long, in terms of accumulated time-temperature increments, export supply chains. In contrast, shaded fruit could be directed into shorter domestic supply chains. As a harvest strategy, segregating fruit lots from harvest could underpin the quality offered to consumers at the end of ‘short’ and ‘long’ supply chains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Challenges in Sustainable Plant Cultivation and Produce Supply)
Open AccessArticle
Predictors of Motivation and Barriers to ICT-Enabling Education for Sustainability
by
, , , , , , and
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 749; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020749 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
There is an increasing interest and effort in reorienting university curricula to address sustainability and preparing teachers to get involved in embedding sustainability and the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in teaching and curricula enabled by Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs). Evidence shows
[...] Read more.
There is an increasing interest and effort in reorienting university curricula to address sustainability and preparing teachers to get involved in embedding sustainability and the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in teaching and curricula enabled by Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs). Evidence shows that this interest and effort is often prevented by various barriers at three levels: teacher- level barriers, school-level barriers, and system-level barriers. In this study, the attempt was geared towards identifying the constituencies of these three levels of barriers and examining the extent to which they predict teachers’ motivation to embed sustainability and SDGs in various school subject areas, including arts-based education. A survey of 1253 teachers in Malaysia revealed that the teacher- and system-level barriers explain 83% of the motivation variance. By identifying, addressing, and investigating these barriers, higher education institutions—and especially teacher education—could be better informed in reorienting university curricula to embed ICT-enabled Education for Sustainability (ICTeEfS). These results were also used in planning and implementing in-service teacher training interventions in the context of a European Commission Erasmus+-funded project.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Teaching and Learning for Embedding Sustainability in Higher Education)
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Atmospheric Deposition of Potentially Toxic Elements in Macedonia Using a Moss Biomonitoring Technique
by
, , , , and
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 748; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020748 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the changes in atmospheric deposition trends in Macedonia, using a moss biomonitoring technique. This technique has been used to assess the content of potentially toxic elements in Macedonia in 2002, 2005, 2010, and 2015, within the framework of
[...] Read more.
This study aims to investigate the changes in atmospheric deposition trends in Macedonia, using a moss biomonitoring technique. This technique has been used to assess the content of potentially toxic elements in Macedonia in 2002, 2005, 2010, and 2015, within the framework of the International Cooperative Program on Effects of Air Pollution on Natural Vegetation and Crops. The content of 42 elements was analyzed using instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA), inductively coupled plasma–atomic emission spectrometry (ICP–AES), and atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS), on 72 moss samples collected in the summer of 2015. The median values of the elements studied were compared with data from previous years and with median values obtained from comparable studies in Norway and the neighboring countries. Through factor and cluster analysis, three geogenic factors were identified: Factor 1, which includes the elements Al, Ce, Fe, Hf, La, Li, Na, Sc, Sm, Tb, Ti, Th, V, and U; Factor 4, which includes As, Cl, and I; and Factor 5, which includes the elements Ba and Sr. In addition, one geogenic-anthropogenic factor containing Co, Cr, and Ni (Factor 2), was identified, and one anthropogenic factor containing Cd, Pb, Sb, and Zn (Factor 3). The lead and zinc mines near the towns of Kriva Palanka, Probištip, and Makedonska Kamenica in the eastern region of the country, the former lead and zinc smelter in the town of Veles, and the ferronickel smelter near Kavadarci, have continuously had the greatest anthropogenic impact on the atmospheric deposition of potentially toxic elements during the time period of the study. In addition to the human influences, the lithology and the composition of the soil continue to play a significant role in the distribution of the elements.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Atmospheric Pollution and Air Quality Studies)
Open AccessArticle
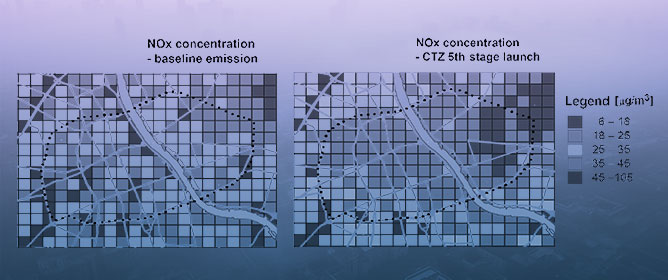
Microscale Investigation of Urban Heat Island (UHI) in Annaba City: Unveiling Factors and Mitigation Strategies
by
, , , and
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 747; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020747 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Cities are facing significant challenges related to climate change, particularly due to the increasing impact of the Urban Heat Island (UHI) phenomenon. The present study investigated the UHI phenomenon at the microscale in Annaba, Algeria. The research involved a multi-step approach, starting with
[...] Read more.
Cities are facing significant challenges related to climate change, particularly due to the increasing impact of the Urban Heat Island (UHI) phenomenon. The present study investigated the UHI phenomenon at the microscale in Annaba, Algeria. The research involved a multi-step approach, starting with on-site measurements of urban microclimate parameters, performed in downtown Annaba on 6 July 2023. The UHI intensity was quantified by comparing city-measured temperatures with rural surroundings. Thermal imaging is then used to empirically identify the contributing factors to UHI initiation at the microscale. The study employed the ENVI-met model to analyse mitigation strategies, manipulating parameters for six scenarios including the current design of the study area. Outputs were used to assess the impact of these strategies on air temperature, mean radiant temperature, relative humidity, and wind speed. The findings revealed an intense UHI effect in Annaba city with a peak difference of 6.9 °C, with practical implications for buildings, ground and roads, vehicles, air conditioners, and specific facade materials. Introducing urban vegetation, particularly urban trees and green roofs, proved highly effectiveness in mitigating the UHI in downtown Annaba. Urban trees demonstrated the most substantial impact, reducing temperatures by 1.9 °C at 1 p.m., while green roof temperature reductions ranged from 0.1 °C to 2 °C.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urban Overheating in a Context of Climate Change: Measurements, Modeling, Thermal Comfort and Adaptation Strategies)
►▼
Show Figures
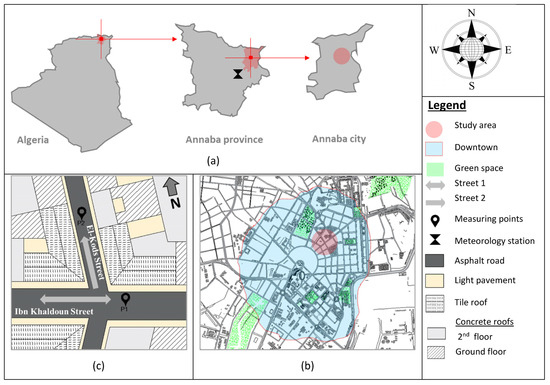
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of the Thermal Properties of Buildings in Eastern Almería (Spain) during the Summer in a Mediterranean Climate
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 746; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020746 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Within a context in which temperatures are increasing due to global warming, it is important to assess the capacity of buildings, old and modern, to respond to this new situation. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of understanding more about the thermal properties
[...] Read more.
Within a context in which temperatures are increasing due to global warming, it is important to assess the capacity of buildings, old and modern, to respond to this new situation. Recent studies have highlighted the importance of understanding more about the thermal properties of traditional constructions. This study quantifies the impact of the high summer temperatures typical of the Mediterranean climate on traditional farmhouses in Eastern Almería (Spain). The study group of farmhouses was divided into three models representative of the different types of Eastern Almería vernacular architecture. Energy consumption in the three models was simulated using EnergyPlus. The three models were assessed in free-floating conditions. The window-to-wall ratio and U-factor values were studied in order to evaluate potential benefits in terms of energy efficiency. Outdoor and indoor temperatures were compared. Finally, an adaptive thermal comfort analysis was performed according to ASHRAE 55. Results highlight the ability of Eastern Almería farmhouses to mitigate extreme temperatures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards Carbon Neutrality: Recent Advances in Sustainable Building Energy and Thermal System Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Extreme Random Uncertainty in Energy and Environment Systems for Coal-Dependent City by a Copula-Based Interval Cost–Benefit Stochastic Approach
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 745; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020745 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Extreme random events will interfere with the inversion analysis of energy and environment systems (EES) and make the planning schemes unreliable. A Copula-based interval cost–benefit stochastic programming (CICS) is proposed to deal with extreme random uncertainties. Taking Yulin city as an example, there
[...] Read more.
Extreme random events will interfere with the inversion analysis of energy and environment systems (EES) and make the planning schemes unreliable. A Copula-based interval cost–benefit stochastic programming (CICS) is proposed to deal with extreme random uncertainties. Taking Yulin city as an example, there are nine constraint-violation scenarios and six coal-reduction scenarios are designed. The results disclose that (i) both system cost and pollutant emission would decrease as the industrial energy supply constraint-violation level increases; (ii) when the primary and secondary energy output increases by 9% and 13%, respectively, and industrial coal supply decreases by 40%, the coal-dependent index of the system would be the lowest, and the corresponding system profitability could reach [29.3, 53.0] %; (iii) compared with the traditional chance-constrained programming, Copula-based stochastic programming can reflect more uncertain information and achieve a higher marginal net present value rate. Overall, the CICS-EES model offers a novel approach to gain insight into the tradeoff between system reliability and profitability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Analysis, Planning and Management of Energy and Atmospheric Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
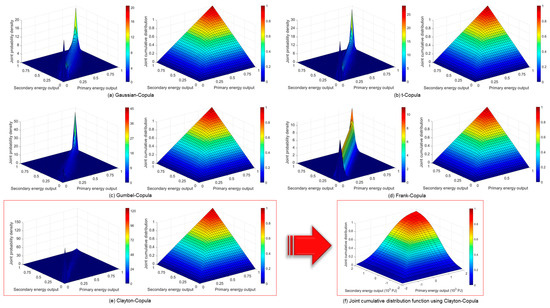
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Building a Life Cycle Carbon Emission Estimation Model Based on an Early Design: 68 Case Studies from China
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 744; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020744 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
The building sector contributes to 50.9 percent of China’s carbon emissions. Due to the complexity of the assessment process, it is difficult to predict the entire life cycle carbon emissions of a building at the early stage of design. In this study, a
[...] Read more.
The building sector contributes to 50.9 percent of China’s carbon emissions. Due to the complexity of the assessment process, it is difficult to predict the entire life cycle carbon emissions of a building at the early stage of design. In this study, a whole-life carbon emission estimation model for the early stage of building design is developed based on comparison of the standard calculations and an analysis of stock cases. Firstly, the standard calculation methods in China, Japan and Europe were compared, and the boundary of the model was defined in three parts: production, construction and demolition and operation. Second, information on 68 examples of Chinese buildings was collected and divided into a training set and a test set at a ratio of 7:3. In the training set, the relationship between carbon emissions and the design parameters was searched, and a carbon emission estimation model applicable to different stages was constructed. Finally, the model was applied to the test set for validation. The results show that the calculation error of the model is within ±15%, and it can quickly estimate carbon emissions based on the design factors, which is helpful for carbon emission assessment work in the early stages of design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Construction: Green Building Design)
►▼
Show Figures
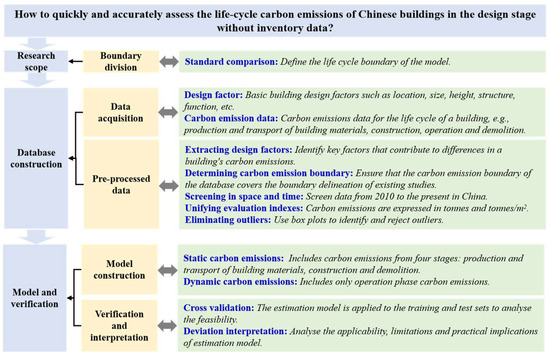
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of External Environment Design for Libraries in Hot and Dry Regions during Summer
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 743; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020743 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
To address the poor thermal comfort of library exteriors in hot and dry regions during the summer, this study takes the libraries of universities in Xinjiang as its research object. It corrects the range of the perceived environmental temperature (PET) index for evaluating
[...] Read more.
To address the poor thermal comfort of library exteriors in hot and dry regions during the summer, this study takes the libraries of universities in Xinjiang as its research object. It corrects the range of the perceived environmental temperature (PET) index for evaluating comfort in Xinjiang by combining subjective and objective methods. It explores the impact and adjustment mechanism of physical parameters on PET through field measurements and simulations. Finally, it determines the optimal external environmental design based on PET. The research results show that the neutral temperature of PET in Xinjiang during the summer is 27.44 °C, and the optimal comfort temperature range is 25.52–29.36 °C. The correlation between meteorological and physical parameters and PET is as follows: Tg > G > Ta > RH > SVF > reflectance > Va. The optimal PET design includes a combination of a water body in the upwind direction on the south side, an asphalt underlay, grass, and large-leaved wax vegetation. In the optimal scheme, PET decreased by 6.73 °C, or 12.59%, compared with Case 0 at 18:00. This study provides a reference for the design of external environmental conditions in hot and dry regions during the summer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental Governance and Environmental Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures
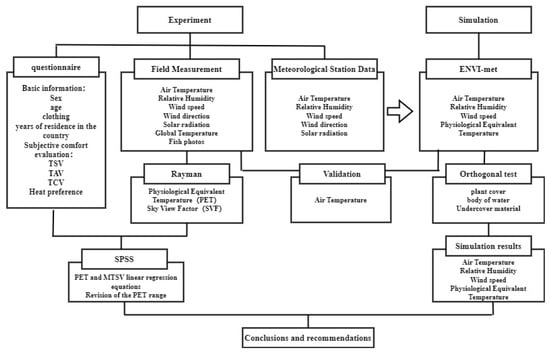
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Modular IoT-Based Architecture for Logistics Service Performance Assessment and Real-Time Scheduling towards a Synchromodal Transport System
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 742; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020742 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Logistics is significantly impacted by quality/quantity issues associated with data collection and data sharing restrictions. Nonetheless, public data from national entities and internet-of-things (IoT) solutions enable the development of integrated tools for performance analysis and real-time optimization of logistics networks. This study proposes
[...] Read more.
Logistics is significantly impacted by quality/quantity issues associated with data collection and data sharing restrictions. Nonetheless, public data from national entities and internet-of-things (IoT) solutions enable the development of integrated tools for performance analysis and real-time optimization of logistics networks. This study proposes a three-module data-driven system architecture that covers (a) logistics data collection tools, (b) logistics services performance evaluation, and (c) the transition to synchromodal systems. Module 1 integrates multisource data from national logistics platforms and embedded devices placed within intermodal containers. A multigraph representation of the problem is conceived. Environmental, economic, and operational data are generated and injected into a digital twin. Thus, key performance indicators (KPIs) are computed by simulation or direct transformation of the collected data. Module 2 uses Multi-directional Efficiency Analysis, an optimization algorithm that benchmarks multimodal transportation routes of containers using prior KPIs. Outputs are a technical performance index relevant to logistics clients and improvement measures for logistics service providers. A real case study application of the solution proposed for Module 2 is presented. Module 3 provides real-time scheduling and assignment models using CP-sat solvers, accommodating varying system dynamics and resource availability, minimizing makespan and operational costs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Supply Chain & Logistics System Evolutions: Achieving Innovative Industrial Platforms and Digital Ecosystem Transformation)
►▼
Show Figures
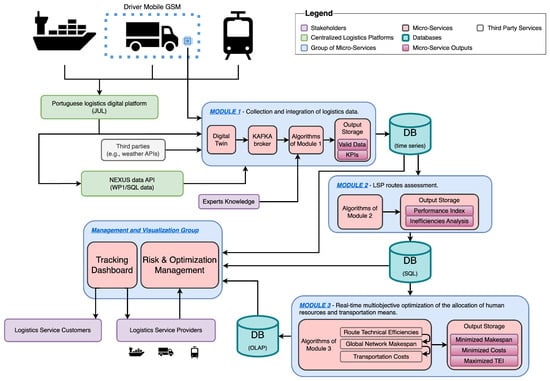
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Relationships between Sustainable Operations and the Resilience of SMEs
by
and
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 741; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020741 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
In the 21st century, the primary concerns within our society and economic framework revolve around securing a sustainable future and ensuring our future prospects. The crises witnessed in recent years have both introduced new challenges and revived existing difficulties. The crucial question emerges:
[...] Read more.
In the 21st century, the primary concerns within our society and economic framework revolve around securing a sustainable future and ensuring our future prospects. The crises witnessed in recent years have both introduced new challenges and revived existing difficulties. The crucial question emerges: can societies and economies demonstrate the resilience necessary to avert impending dangers during such circumstances? This consideration holds particular significance for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) operating in the global economy. SMEs play a vital role in national economies, and their importance is even more pronounced within our national societies. Addressing threats and challenges in the SME sector proves to be more challenging due to their compact size, which lacks the protective shield against various environmental impacts enjoyed by larger enterprises with their greater size and capabilities. On the other hand, due to their smaller size, SMEs may be able to overcome these obstacles more successfully than large enterprises by using the appropriate tools and investing in opportunities. The aim of this article is to investigate to what extent environmental protection investments and other sustainability-related developments increase the resilience of SMEs. In connection with the above mentioned, it was investigated how the combination of marketing communication and sustainability goals, and how appropriate communication of sustainability, contributes to increasing the resilience of Hungarian SMEs. The analysis is based on a grouping of 266 small and medium-sized enterprises using the variables created based on the literature review and expert interviews.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Development of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: Resilience, Creativity and Learning)
►▼
Show Figures
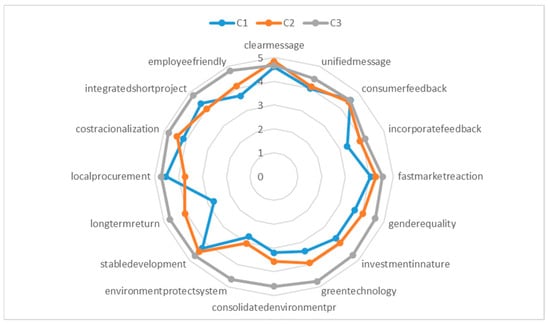
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Economic Analysis of the Use of Local Natural Waste: Volcanic Ash of Mt. Etna Volcano (Italy) for Geopolymer Production
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 740; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020740 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
This paper analyses the net social benefits deriving from the medium-scale production of geopolymers based on volcanic ash compared to traditional cementitious materials used in construction and restoration sectors. In contrast to the existing literature grounded on the physical and mechanical characterization of
[...] Read more.
This paper analyses the net social benefits deriving from the medium-scale production of geopolymers based on volcanic ash compared to traditional cementitious materials used in construction and restoration sectors. In contrast to the existing literature grounded on the physical and mechanical characterization of geopolymers, our analysis considers two aspects: public finance savings from avoiding the disposal of volcanic ash in landfills and environmental benefits deriving from reduction in CO2 releases due to the production process at room temperature. Our case study focuses on the reuse of natural waste, namely the volcanic ash of the Mt. Etna volcano (Italy), whose disposal involves significant costs for society. Its use in the alkaline activation process avoids the exploitation of natural resources. Considering the huge amount of volcanic ash from Mt. Etna that falls on the urban areas of Eastern Sicily, the results show relevant economic benefits, in terms of both avoided costs and tax reductions for the citizens. Alongside these, significant environmental benefits are evidenced thanks to the release of up to 78% lower CO2 emissions by synthesised materials with volcanic ash than by traditional cementitious ones. Overall, the social cost savings compared to traditional materials is 0.339 EUR/kg for geopolymer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Materials for Sustainability: From Laboratory to Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
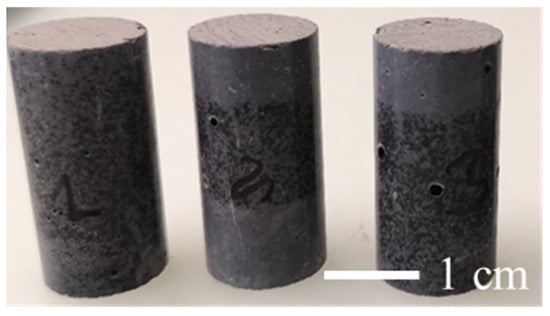
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Real Estate “COVID” Factors on Expressed Satisfaction of Residents during COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 739; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020739 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
This article addresses research questions on participants’ satisfaction with the essential “COVID” factors of home ownership during the COVID-19 pandemic. It analyses statistically significant differences in participants’ demographic characteristics in relation to the various “COVID” factors. The main instrument used to measure the
[...] Read more.
This article addresses research questions on participants’ satisfaction with the essential “COVID” factors of home ownership during the COVID-19 pandemic. It analyses statistically significant differences in participants’ demographic characteristics in relation to the various “COVID” factors. The main instrument used to measure the participants’ satisfaction was a questionnaire from our previous study in 2010. The participants expressed as the most important “COVID” factors the possibility of setting up a home office, internet in the flat and the possibility of setting up a mudroom, a separate, independent space and contact with nature, which can include good natural lighting and ventilation. The results show that the statistically significant differences between the year 2010 and 2021 in terms of living conditions in the property are expressed in the participants’ satisfaction with their current living conditions, brightness of natural light, proximity to kindergartens, schools, work opinions and health centres, maintenance costs and sense of belonging to the neighbourhood. This understanding gives our study a special significance. Our study investigates the parameters of the interior of properties, so in the future, it would make sense to expand the studies in this field to include living parameters, the building, the surroundings and the neighbourhood.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Investigation and Research of Sustainable Innovation in Built Environment)
►▼
Show Figures
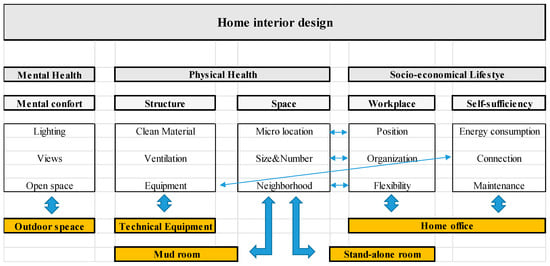
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Planning and Construction of Intercity Railways on the Economic Development of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration: An Analysis Based on the Spatial Durbin Model
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 738; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020738 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Efficient transportation is essential for regional economic development. Currently, the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration is accelerating the construction of intercity railways in the region to strengthen the links between cities. To provide a more detailed account, this study examined data spanning the
[...] Read more.
Efficient transportation is essential for regional economic development. Currently, the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration is accelerating the construction of intercity railways in the region to strengthen the links between cities. To provide a more detailed account, this study examined data spanning the years 2010–2021 across nine key cities in the Pearl River Delta. Employing a spatial Durbin model, we sought to uncover specific spatial patterns associated with intercity railways, particularly their pronounced impact on neighboring cities. Our quantitative findings, derived from the spatial Durbin model, revealed a statistically significant positive contribution of intercity railways to overall regional development. Contrary to initial concerns, the results indicate that intercity railways contribute significantly without exacerbating existing imbalances. However, according to the decomposition analysis of effects, most coefficients of the explanatory variables with a direct effect were found to be positive and significant, indicating their positive impact, while those with an indirect effect were found to be nonsignificant, suggesting that the effect of planning and construction of intercity railways on the economic development of the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration is currently at a stage of factor concentration. In conclusion, our study emphasizes the need for prioritizing regional connections in intercity railway construction. This strategy can facilitate production factor flow and foster the proactive development of transportation infrastructure, thereby ensuring a balanced and sustainable regional economic growth trajectory.
Full article
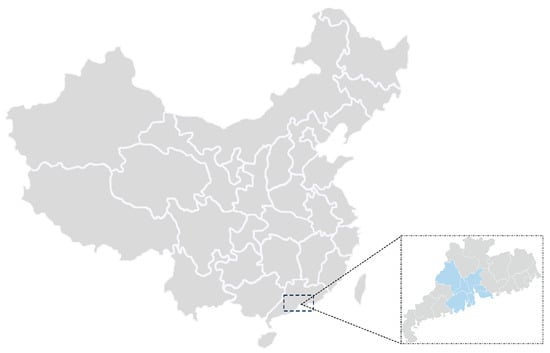
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Non-Destructive Analysis Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Predict Albumin, Globulin, Glutelin, and Total Protein Content in Sunflower Seeds
by
, , , , , , and
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 737; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020737 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
This pilot study explores the potential of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for predicting sunflower seed protein content, focusing on both crushed and husked samples to address agricultural sustainability concerns. Sunflower seeds are renowned for their richness in both oil and protein content. The important
[...] Read more.
This pilot study explores the potential of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for predicting sunflower seed protein content, focusing on both crushed and husked samples to address agricultural sustainability concerns. Sunflower seeds are renowned for their richness in both oil and protein content. The important role of sunflower seeds in the food and feed industries underscores the importance of using precise analytical tools to determine their composition. In essence, the nature of the hull of sunflower seeds, which skews the interaction between the seed and light, necessitates a sophisticated analysis. This study analyzes 326 samples using a near-infrared spectrometer to develop robust partial least squares (PLS) models. High accuracy is achieved in predicting total protein for crushed samples (r²c = 0.97, RMSEC 0.54%, RPDc 6; r²p = 0.78, RMSEP 1.24%, RPDp 2.1). Extending the scope to husked samples, promising results emerge for crude protein prediction (r²c = 0.93, RMSEC 0.86%, RPDc 3.9; r²cv = 0.83, RMSECV 1.39%, RPDcv 2.4). Additionally, this study delves into protein fractions (globulin, albumin, and glutelin) in crushed seeds, adding depth to the analysis. In conclusion, NIR spectroscopy proves valuable for rapid prescreening in breeding, especially when working with hulled grains, offering non-destructive efficiency and predictive accuracy in agricultural analysis. The novel exploration of protein fractions in sunflower seeds further enhances this study’s importance, providing a valuable contribution to the field and underscoring the practical applications of NIR spectroscopy in sustainable agriculture. In conclusion, the opacity of sunflower seed hulls poses challenges in infrared spectroscopy, limiting light penetration and accuracy. Dehulled seeds are preferred for reliable results, overcoming hull-related limitations. Although grinding provides the advantages of uniformity and reproducibility for near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, the preference for dehulled grains persists. The practical need for accurate analysis in agriculture and breeding drives the choice of spectroscopy on dehulled seeds, allowing for replanting.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Technology in Agricultural Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
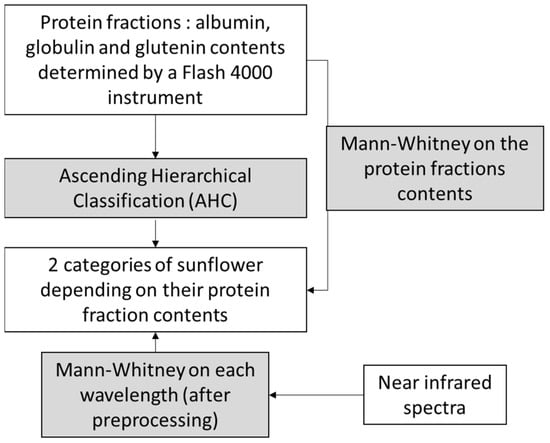
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bioconversion of Agroindustrial Asparagus Waste into Bacterial Cellulose by Komagataeibacter rhaeticus
by
, , , , , , , , , , and
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 736; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020736 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Bacterial cellulose is a biomaterial known for its physical and mechanical properties, including its high mechanical strength, water retention capacity, and biocompatibility. Its production from various carbohydrates has been widely studied, aiming to find more efficient and cost-effective culture media. This study investigated
[...] Read more.
Bacterial cellulose is a biomaterial known for its physical and mechanical properties, including its high mechanical strength, water retention capacity, and biocompatibility. Its production from various carbohydrates has been widely studied, aiming to find more efficient and cost-effective culture media. This study investigated the production of bacterial cellulose from agroindustrial asparagus peel waste by Komagataeibacter rhaeticus QK23. A strain of QK23 was isolated and cultivated from a kombucha tea, identified based on morphological and molecular characteristics using the 16S rRNA gene. The waste was hydrolyzed and converted into fermentable sugars. Using the response surface methodology, the inoculum dose (1–20%) and incubation time (3–25 days) were evaluated concerning bacterial cellulose yield. The results demonstrated that with an optimal inoculum dose of 10.5% and an incubation time of 25 days, a production of 2.57 g/L was achieved. It was characterized as similar to type I cellulose, exhibiting a high degree of crystallinity (81.89%) and suitable morphological properties, evidenced by a fiber size of 178 nm and a surface roughness of 27.05 nm. Converting asparagus waste into bacterial cellulose is a sustainable and effective strategy that promotes the development of advanced biomaterials in biotechnology research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recycling Biomass for Agriculture and Bioenergy Production)
►▼
Show Figures
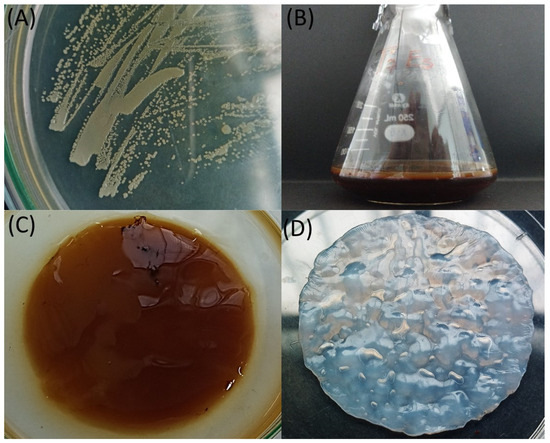
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Spatial Dynamic Evolution of Digital Agriculture—Evidence from China
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 735; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020735 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Digital agriculture serves as a pivotal means of ushering in innovative agricultural practices and achieving sustainable agricultural development. Although agricultural digitalization has received increasing attention, the unbalanced development and regional disparities of digital agriculture are still key obstacles to sustainable agricultural development. Based
[...] Read more.
Digital agriculture serves as a pivotal means of ushering in innovative agricultural practices and achieving sustainable agricultural development. Although agricultural digitalization has received increasing attention, the unbalanced development and regional disparities of digital agriculture are still key obstacles to sustainable agricultural development. Based on the data of 31 provinces in China from 2013 to 2021, this study evaluates the development level of digital agriculture in China, and further analyzes the distribution pattern, spatial characteristics, and transition probabilities of digital agriculture from a regional perspective. The index system of the digital agriculture development level is constructed from five aspects: infrastructure, talent resources, agricultural informatization, the digitization of agricultural production processes, and agricultural production efficiency. Among these, infrastructure and talent resources reflect the resources needed for the development of digital agriculture; agricultural informatization and the digitization of the agricultural production process indicate the role of digitization in the process of agricultural development; and the agricultural production efficiency is the goal of the digital agriculture development, which is a critical criteria of its evaluation. The weighted analysis method of objective sequential analysis, which combines the dynamic level of indicators and sequential relationships, is used to assign weights to the indicators. In addition, to address the regional disparities in the development level of digital agriculture, kernel density estimation, Moran’s index, and (spatial) Markov chain analysis are applied to analyze the spatial dynamic evolution of digital agriculture in China. The findings reveal substantial regional disparities in digital agriculture development within China, particularly in the Western region, where development lags behind. Moreover, this study offers actionable policy recommendations for policymakers to strengthen regional infrastructure and talent cultivation, as well as other aspects of digital agriculture development, to mitigate regional differences and provide reference for other emerging countries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Rural Development, Agricultural Economics and China's Economy Research)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Considering Historical Land Use When Estimating Soil Carbon Stock Changes of Transitional Croplands
Sustainability 2024, 16(2), 734; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020734 - 15 Jan 2024
Abstract
Understanding changes to soil organic carbon storage (SOC) requires knowledge of detailed land use history. Many satellite-based analyses of land use change have been conducted over short periods (typically 5 to 10 years) to investigate causality to a demand increase in an agricultural
[...] Read more.
Understanding changes to soil organic carbon storage (SOC) requires knowledge of detailed land use history. Many satellite-based analyses of land use change have been conducted over short periods (typically 5 to 10 years) to investigate causality to a demand increase in an agricultural commodity. However, statistically significant changes in SOC are not readily observable during this time and typically require decades for meaningful differences to accrue. This study aimed to determine land use and soil organic carbon stocks on land parcels over 36 years (1985–2021) located in areas where historical land use transitions between cropland and non-cropland are prevalent. Aerial and satellite imagery were analyzed across 25,992 hectares in ten counties across the Corn Belt. Grower interviews were conducted to solicit feedback on the drivers of land use change. Finally, SOC analyses associated with land use changes were determined using two process-based models. Analysis showed that 371 of the parcels had remained in cropland, 611 parcels transitioned into non-cropland, and 18 parcels were identified as non-cropland. The grower surveys indicated that the most common reasons for returning land to crop was the difficulty getting land re-enrolled in the CRP and reduced cattle prices. Both the SALUS and GREET-CCLUB models were parameterized to assess soil carbon changes for the respective land use history, and both models returned consistent SOC increases at the county level over time.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biofuel-Induced Land Use Changes: Theory, Modeling Practices, Historical Observations, and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures
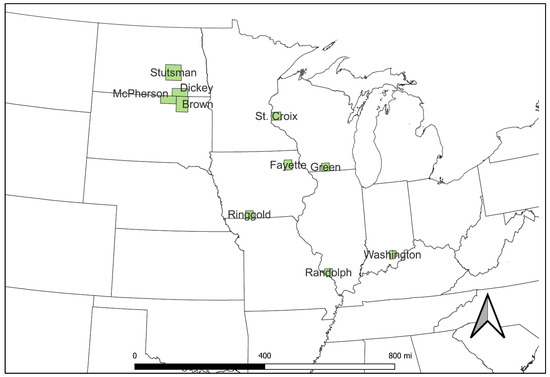
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Sustainability Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Computers, Electronics, Micromachines, Sustainability
Innovation of Applied System
Topic Editors: Sheng-Joue Young, Shoou-Jinn Chang, Liang-Wen JiDeadline: 31 January 2024
Topic in
Electricity, Electronics, Energies, Processes, Sustainability
Sustainable Solutions for a Sustainable Future in the Natural Gas and Electricity Markets
Topic Editors: Helena Martin, Jordi de la Hoz, Pere PalacínDeadline: 15 February 2024
Topic in
Energies, Processes, Water, Sustainability, Buildings
Towards a Greener Tomorrow—Modern Trends in Cooling and Water Solutions
Topic Editors: Jaroslaw Krzywanski, Marcin Sosnowski, Karol Sztekler, Anna Pajdak, Anna Zylka, Anna Kulakowska, Karolina Grabowska, Dorian SkrobekDeadline: 29 February 2024
Topic in
Horticulturae, Plants, Agronomy, Agriculture, Sustainability
Soil Fertility and Plant Nutrition for Sustainable Agriculture
Topic Editors: Othmane Merah, Purushothaman Chirakkuzhyil Abhilash, Magdi T. Abdelhamid, Hailin Zhang, Bachar ZebibDeadline: 10 March 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable Power System Planning and Analysis
Guest Editors: Paulo M. De Oliveira-De Jesus, Manuel AlvarezDeadline: 20 January 2024
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Microbial Diversity in Cold Environments and Their Sustainable Use
Guest Editor: Masaharu TsujiDeadline: 31 January 2024
Special Issue in
Sustainability
The Impact of Climate Change on the Facades of Tall Buildings
Guest Editors: Michael Yit Lin Chew, Nyuk Wong, Sheila ConejosDeadline: 15 February 2024
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Product Eco-Design in the Era of Circular Economy
Guest Editors: Claudio Favi, Marco MarconiDeadline: 29 February 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Tourism Research and Regional Sciences
Collection Editors: Lóránt Dénes Dávid, Laszlo VASA, Setiawan Priatmoko
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Mobile Technology, Gamification and Artificial Intelligence to Improve Sustainability in Education
Collection Editors: Eloy López Meneses, Esteban Vázquez-Cano, María Elena Parra-González
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Sustainable Soil Management in a Changing Climate
Collection Editors: Georgios Koubouris, José Alfonso Gómez, Luuk Fleskens, Giuseppe Montanaro
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Towards More Walkable and Liveable Cities: Perceptions, Attitudes, Methods, Technologies and Policies
Collection Editors: Fernando Fonseca, Paulo Ribeiro, Elisa Conticelli, George N. Papageorgiou